Monster Energy Drink
The Monster Drink can cause some side effects which is something most people are unaware of. We will talk more about this in the following text. We need energy during the day because there is so much we need to accomplish, and this has made way for energy drinks that provide stamina and energy to finish all the daily chores. The Monster energy drink is one of the most popular of these drinks, but there are some side effects and problems associated with the consumption of this energy drink.
Facts
Caffeine is a part of all energy drinks and the Monster drink as well. There are 106 mg of caffeine in a 16 oz. of Monster drink, and this amount of caffeine can be dangerous if you drink it regularly. Jitters, headaches, high blood pressure, and heart palpitations are some of the most common side effects associated with the consumption of energy drinks.

The side effect that is the greatest threat to the human body is caffeine resistance, which can be caused by regular consumption of energy drinks. This problem will lead to the increased consumption of the drink because it is not causing the effect intended and experienced in the past. Carbohydrates in energy drinks can also lead to some side effects. One energy drink has 27g of carbohydrates, and they can lead to problems with nutrient absorption and food absorption in the bloodstream, which might lead to dehydration, gastrointestinal problems, and other stomach disorders.
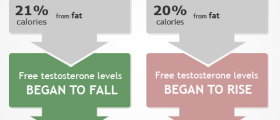
Most energy drinks and the Monster drink as well, contain sugar, and sugar, along with caffeine, is the biggest reason for the energy we gain from these drinks. But the effect of sugar never lasts long, and the effect dies quickly, which is scientifically proven.
The level of sugar in the body drops when this effect ends, which leads to sudden fatigue and laxative effect. Problems with insulin levels can be developed due to the increased sugar levels because of the regular consumption of energy drinks. Seizures, headaches, and trembling are some of the problems that can be caused by insulin level troubles.
Herbs are usually used for the manufacture of energy drinks and some of those included in Monster drinks are ginseng and taurine. If you drink energy drinks in a reasonable amount, there is no danger. Also, all of the stated side effects will not interfere with general health.
- In Europe, they were launched for the first time in 1987; then the market expanded throughout the world, becoming very popular after the launch of Red Bull in 1997. Since then, the energy drink market has grown dramatically, with various brands released worldwide. The annual consumption of energy drinks in 2013 exceeded 5.8 billion liters in around 160 countries.
- The estimated total U.S. retail market value for energy drinks was around 12.5 billion USD in 2012 and the market increased 56% from 2006 to 2002.
- Manufacturers recently have shifted their consumer focus from athletes to young people. Energy drinks are aggressively marketed in places popular with teens and young adults. Approximately, two thirds of energy drink consumers are 13–35 years old, and boys are two thirds of the market. In the U.S., energy drinks are the second most common dietary supplement used by young people; about 30% consume energy drinks on a regular basis.
- Energy drinks are designed to give an “energy boost” to the drinker by a combination of stimulants and energy boosters. The major constituent in most energy drinks is caffeine. They usually contain 80–150 mg of caffeine per 8 ounces, which is equivalent to 5 ounces of coffee or two 12-ounce cans of caffeinated soda.
- Several studies have shown an increase in heart rate and arterial blood pressure after energy drink consumption. These findings were attributed to the ergogenic effects of the caffeine content of the energy drink. In addition, significant cardiac manifestations such as ventricular arrhythmias, ST segment elevation and QT prolongation have been documented following energy drink overconsumption.
- Individuals usually develop symptoms of caffeine intoxication in doses equal to or above 200 mg. Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, gastrointestinal upset, muscle twitching, restlessness, and periods of inexhaustibility.
- Energy drinks usually contain large amounts of sugar ranging from 21 g to 34 g per oz. The sugar content is mainly in the form of sucrose, glucose or high fructose corn syrup. Therefore, high energy drink intake may increase the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- The caffeine in energy drinks has been shown to enhance diuresis. Therefore, energy drinks should be avoided during prolonged exercise in a hot environment because of the potential for dehydration. Studies have reported that dehydration at a level of 1.5% during prolonged exercise may result in an increase in body temperature, heart rate and perceived rate of exertion.
- The large amount of caffeine in energy drinks provides the consumer with the desirable effects of improved memory, increased alertness and elevated mood. The most widely cited study is the one conducted by Alford et al.
- Walsh et al assessed the effects of energy drinks on time to exhaustion during treadmill exercise. They observed a significant increase in time to exhaustion during a moderate intensity endurance run as well as improvement in perceived feelings of focus, energy and fatigue.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...