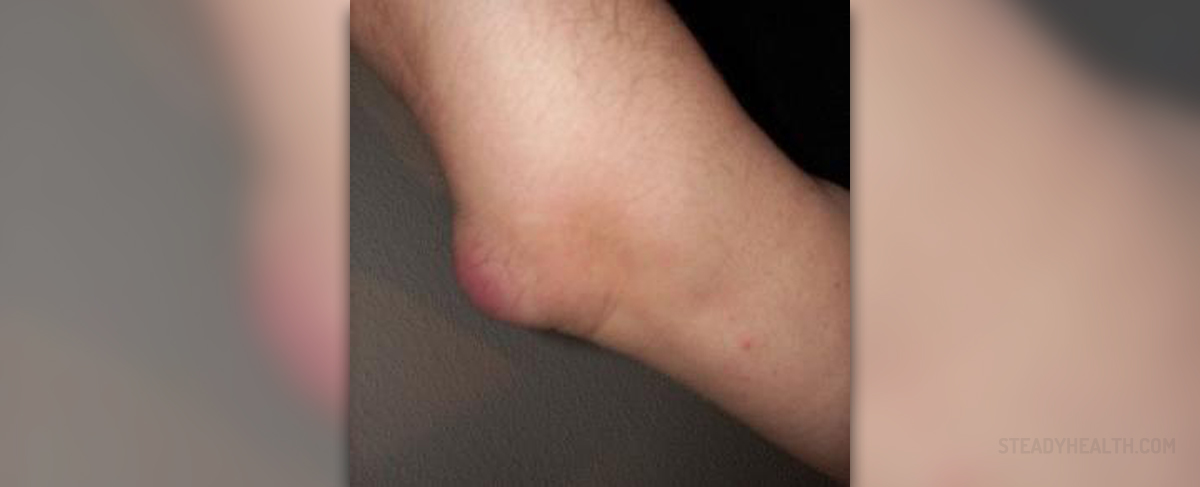
Introduction to Bursitis
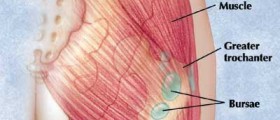
Chronic bursitis is a chronic inflammation of the bursa, which is a sac of lubricating fluid with one purpose; the reduction of friction between the tendons and the bones and joints. Chronic bursitis develops as a consequence of recurring activity that places too much strain on the joint, which can in turn be caused by congenital defects as well.
Unlike acute bursitis, which commonly lasts only for a few days, chronic bursitis represents a long lasting condition. It may linger for several weeks and frequently reoccurs. In case chronic bursitis is left untreated (particularly bursitis in the shoulder) there is an increased risk that the patient will develop calcium deposits. The presence of these deposits is responsible for permanent stiffness of the affected joint.
Chronic bursitis typically features severe pain, swelling, and restriction of movement within the affected joint. It generally affects the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, base of the thumb, hip, knee and Achilles tendon.
Treatment for Chronic Bursitis
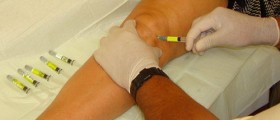
The pain caused by chronic bursitis can be alleviated with hot and cold compresses. This treatment can be applied at home but one must pay attention and never apply cold compresses for longer than 20 minutes. Furthermore, it is essential never to apply ice directly to the skin but first wrap it in clean cloth. Medically, corticosteroids can be prescribed to help reduce inflammation, a procedure that is also available as injections, which have a long lasting effect.
The affected area, whether it is the shoulder, hip, or any other joint, must not be under stress and patients are advised to restrict or limit all movements as much as possible until the pain subsides, which indicates that the bursitis has also remitted. Rest accelerates reduction of swelling. Hence, the pain decreases. Furthermore, patients suffering from chronic bursitis may significantly benefit from physical therapy. An experienced physical therapist will teach a patient how to perform specific exercises that will help a person get his or her joints back in shape.
Surgery is reserved for patients suffering from chronic bursitis who simply do not respond to conservative treatment. The surgeon may recommend incision and drainage of the inflamed bursa in these cases. Prior to the procedure, the skin is numbed with an anesthetic and a surgeon performs a small incision, opens the bursa, and drains the fluid. This is a safe minor surgical procedure.
Furthermore, in some patients chronic bursitis leads to hardening of the bursa and the bursa may also become stiff and calcificated. In such cases, the entire bursa needs to be surgically removed. This type of surgery is generally performed in an outpatient clinic and patients return to their every day activities within 7 to 10 days.
Apart from traditional medicine, some patients also opt to explore alternative medicine to help them with their bursitis symptoms. It is essential to consult a doctor prior to choosing any type of alternative medicine or deciding on the intake of supplements and herbs. Supplements and herbs may, for example, interfere with other medications a person is taking.
The prognosis of acute bursitis is much better than the prognosis for the chronic form of the disease. Still, both of them can be successfully treated or managed, so long as the patient is under the care of a competent doctor.




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...