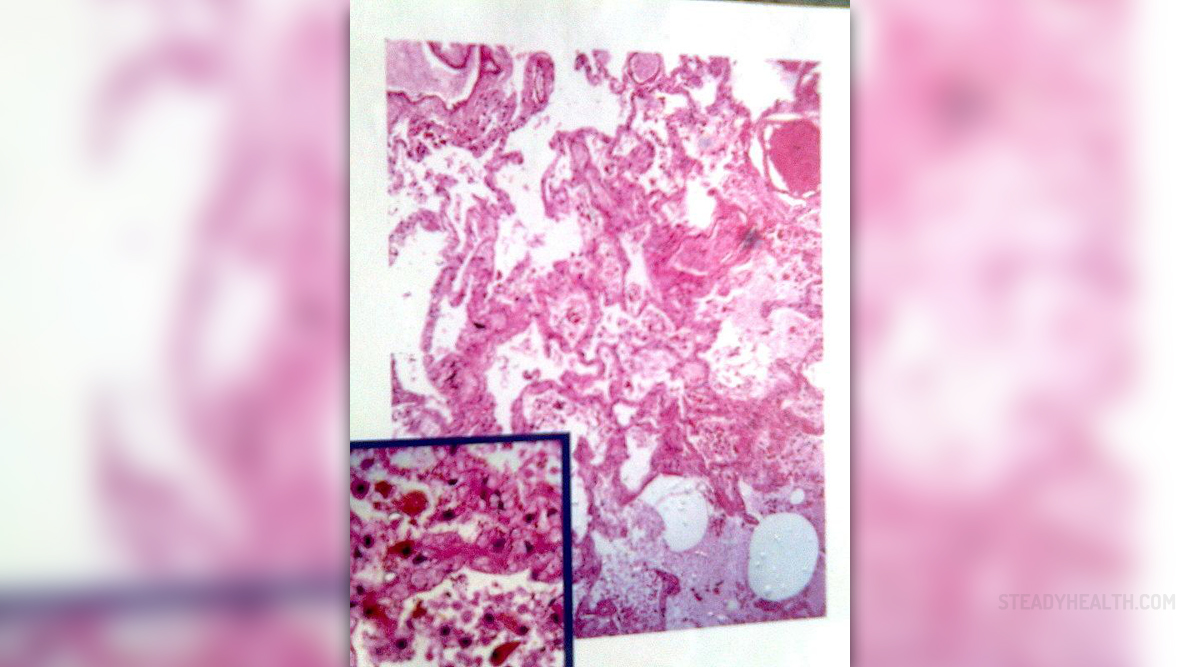
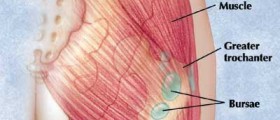
Trochanteric bursitis is a medical term for inflammation of the bursa of the hip, to be more precise inflammation of a fluid-filled sac located at the outside of the hip. Irritation and inflammation of the trochanteric bursa is the cause of pain in the hip.
Causes of Trochanteric Bursitis
There are numerous causes which may trigger inflammation of the trochanteric bursa.
First of all, the problem may result from injury to the hip. Any kind of trauma such as fall onto the hip, bumping the hip into some object or direct blow into the area may cause inflammation of the trochanteric bursa and subsequent pain.
Furthermore, inflammation is associated with overuse of the joint and may result from incorrect posture due to some spinal conditions (scoliosis, arthritis etc).
Arthritis of the hip joint and abnormality like leg length difference are two more potential triggers of trochanteric bursitis.
Trochanteric bursitis may affect people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriasis and thyroid gland disorders. Rarely, it is a side effect of some medications or infections.
And finally, the condition may develop due to previous hip surgery or be closely related to hip bone spurs.Clinical Characteristics of Trochanteric Bursitis
Patients commonly complain about pain localized outside of the hip and thigh or in the buttock. Such pain intensifies while lying on the affected side and the entire area may be tender to touch. Any activity which involves movement of the affected hip (e.g. getting up from a deep chair, getting out of a car etc) only aggravates the pain.Treatment for Trochanteric Bursitis
Treatment for trochanteric bursitis has several goals. It is supposed to reduce pain and eliminate inflammation. Additionally, treatment should preserve motility and prevent recurrence of inflammation. And one more important goal is prevention of potential disability.
Initial care includes adequate bed rest, hot or cold compresses (applied according to doctor's recommendations) and use of splints. The previously mentioned is sufficient enough for some patients to fully recover.
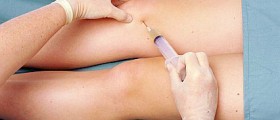
However, a certain number of patients require more complex treatment. Intensive pain is generally relieved with certain NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen. In case these are inefficient, doctors may prescribe corticosteroid injections.
Physical therapy for patients suffering from trochanteric bursitis comprises a set of exercises and splinting. And finally, if all of the mentioned fails to provide with optimal and desirable results, patients are left with only one more treatment modality - surgery.
Trochanteric bursitis may be in some individuals prevented. For example, inflammation associated with overuse of the hip joint can be prevented if one takes it slow and gradually build up his/her activity level. The occurrence of pain during physical activity or exercise should be an alarming sign and if it occurs, one should immediately stop exercising.



-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)
-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...