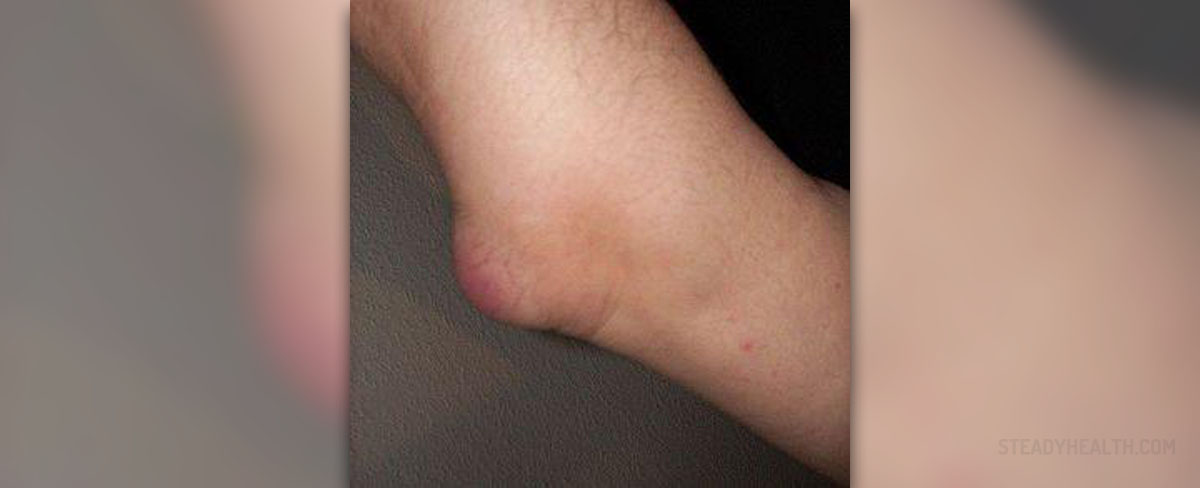
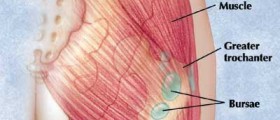
Our bodies contain one hundred and sixty bursae. Bursae are tiny sacs filled with fluid that help reduce friction between bodily tissue. The most important bursae are located near large joints like the elbows, hips, knees and shoulders. Bursae can become inflamed as a result of infection, injury or because of an underlying rheumatic condition. Injuries to bursae can occur in a situation as harmless and seemingly everyday as lifting a bag of groceries into a car.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms will vary depending on the degree of inflammation. In many cases, injury of this type will lead to tenderness and pain around the site of the injury. Swelling, stiffness, redness and localized warmth can all occur due to bursitis. Inflammation and injury such as this can lead to problems with regard to the application of body pressure. For example, one might have difficulty in lying down in the case of hip bursitis, or putting the knees together in the case of knee bursitis.
Bursitis will be identified mainly through the examination of symptomatic problems. Localized pain, swelling, tenderness and pain whilst moving can all be good indications of the presence of bursitis. In addition to this symptomatic diagnosis, x-ray testing can also help in the detection of calcifications in the bursa. This is especially true if bursitis is chronic or recurrent.
Treatment
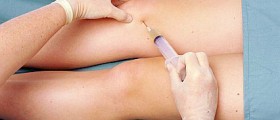
Treatment for bursitis will depend on the root cause. For example, bursitis caused by infection will require different treatment to non-infectious causes. Bursitis that is non-infectious can be treated through the employment of ice compresses, rest and anti-inflammatory and pain medications. In some cases, aspiration of the bursa fluid might be necessary. Non-infectious bursitis can also be addressed through the administration of cortisone into the swollen bursa. It might be the case that this is undertaken at the same time as the aspiration procedure. This will help to rapidly reduce inflammation.
Infectious bursitis will require more serious evaluation. Bursal fluid might be examined in a lab in order to identify the cause of the infection. Antibiotic therapy might be required, as might repeated fluid aspiration. Antibiotics might be given intravenously. Surgical procedures, to drain the infected bursa sac might also be a requirement for this type of problem. In this case, the joint related to the infected bursa will regain full functionality as soon as the surgical wound has fully healed. The surgical operation is known as a bursectomy.




-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...