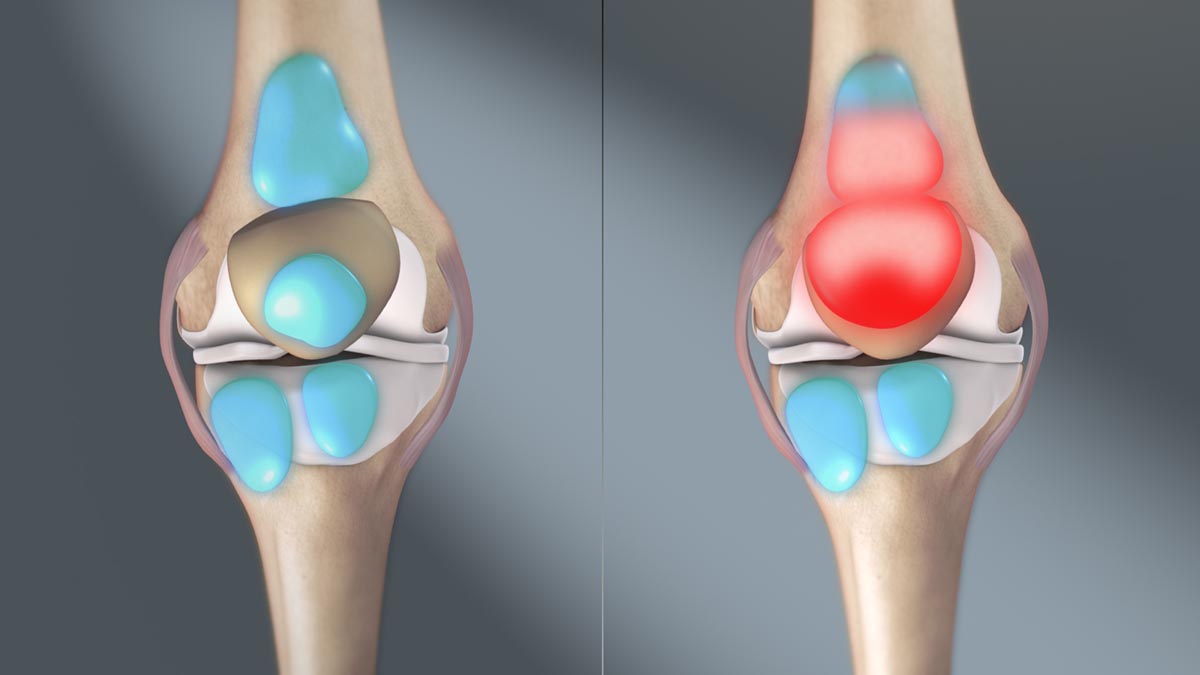
Definition of bursitis
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa, which is a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion which prevents friction between tendons, joints and bones. Most commonly affected are large joints, such as elbows, shoulders, ankles, knees and hip. Bursitis causes pain and stiffness in affected joints and surrounding tissues.
Bursitis can be acute and the symptoms are sharp and sudden pain after the injury, or chronic, which is repeated inflammation of the same area or joint.
Diagnose of bursitis
To accurately diagnose bursitis, your doctor must physically examine you. Also, X-ray, MRI or blood tests are sometimes needed. X-rays are used to establish the possibility of arthritis, calcium deposits or bone abnormalities. Blood test is done in order to relieve additional problems, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Physical examination by your doctor will determine the exact nature of your injury.
Causes of bursitis
Most commonly, causes of bursitis are cases when people are overusing some of their joints in excessive physical activities, such as uncomfortable footwear, extensive and prolonged running, sitting or repeating movements. There are some professional athletes who have this disorder more that others, such tennis players. Also, at higher risk are people with infection, gout or arthritis.
Symptoms and Signs of bursitis
Usually signs and symptoms of bursitis may be loss of free motion in affected areas, swelling, pain in the areas of the bursa, dull ache or stiffness in areas around big joints, worsening pain with pressure or motion, etc.
Treatments for bursitis
Treatments for bursitis usually includes applying cold in cases of acute inflammation, special kinds of massages, hydrotherapy and other physical treatments, applying heat for chronic inflammation, immobilizing of affected joint or area and removing the extra fluid from swollen bursa by syringe.
In some cases anti-inflammatory and pain medication is prescribed. Chronic bursitis concurrently reappears in the same places, while acute bursitis usually lasts one or two weeks.
Prevention of bursitis
You can protect yourself from bursitis occurring or reoccurring, by trying to always place your affected joints on soft cushions, by avoiding overuse of joint or limbs either in hard labors or in recreation and sports, to strengthen the muscles regularly, to try to avoid kneeling or sitting on hard surfaces for prolonged periods of time, by keeping in good shape at all times, by using comfortable chairs, by taking more breaks when you do excessive exercise or heavy labor and by doing appropriate warm-up and cool-down exercises.





-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...