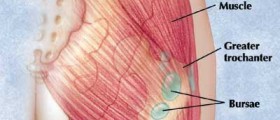
An inflammation of the cavity that lies between a tissue and skin, or between a tissue and bone is called bursitis. When the cavity becomes inflamed, it provokes a pain. Bursitis usually has an effect on the hip, shoulder, elbow and knee. Other areas where it may occur involve the Achilles tendon and the foot. Trochanteric bursitis is the irritation of the cavity at the outside (lateral) point of the hip. It causes pain on the side of the hip, which makes it difficult to lie on the defected side. The inflammation of the hip can be caused either by a direct blow to the area or by constant friction of the iliotibial band on the cavity, as happens throughout long-distance running, climbing, or standing for long periods of time. Also, trochanteric bursitis can develop due to earlier surgery around the hip or prosthetic implants in the hip; arthritis of the lumbar (lower) spine, scoliosis and other spine conditions; pressure on the soft tissues as a consequence of an atypical or failing positioned joint or bone (leg length differences); hip bone spurs or calcium sediments in the ligaments that join to the trochanter. Other diseases or disorders such as thyroid condition, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis can also be related to this condition. Bursitis is often associated with older people.
Tests, diagnosis and treatment
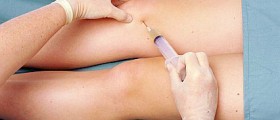
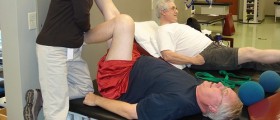
The physician may order an X- ray of the defected area. On rare occasions, blood work may be necessary to eliminate infection or connective-tissue condition. Treatment aims consist of diminishing pain and inflammation, and preventing its reoccurrence. Therapy may consist of cold application to reduce swelling, resting, and splints. In addition, a doctor may recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen, which help in diminishing the pain and swelling. Sometimes, the doctor will suggest exercises to strengthen the muscles in the area. In many situations, especially in chronic cases of hip bursitis, a corticosteroid injection may be advised. Mostly, the surgeon will only carry out the surgical procedure for trochanteric bursitis when he notices some apparent reason for the pain and when he decides that the procedure will help in treatment of the disorder. It may include loosening the iliotibial band, or calcified tissue may be removed. After the surgery, the patient should try to avoid a lot of activity for some time. The rehabilitation after the procedure can be a pretty slow process. The patient will probably go on physical therapy for several weeks. Some of the potential complications are related to infection, nerve or blood vessel injury, deep venous thrombosis, and failure of the operation.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...