Introduction
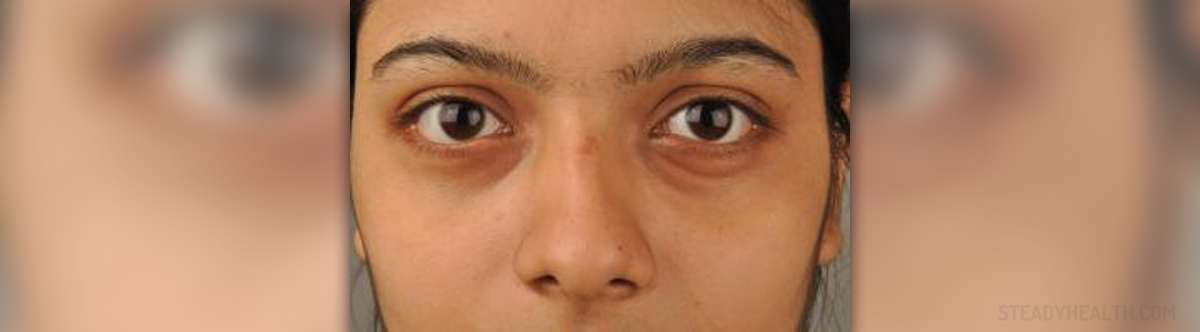
Swollen under eye is a condition that every one of us has experienced. It is not unusual to notice a swollen under eye when we wake up in the morning. This condition is, in the majority of cases, only a symptom of some underlying problem around the eye. Swollen under eye is usually called under eye bags or puffy eyes. This condition manifests through the appearance of characteristic swelling in the tissues that cycle our eyes. These tissues around the eyes are usually called orbits.
Since the skin around the eyes is very sensitive and thin, swollen under eye is an easy noticeable condition. In most cases, swollen under bags tend to disappear by themselves only after a proper rest. Sometimes, they must be treated with certain medications and remedies. However, there are cases when puffy eyes are accompanied by a number of other symptoms, such as itching, pain, irritation and distorted vision. In such cases, the puffy eyes are only a symptom of a serious eye problem and medical advice should besought.
Causes of Swelling Under Eye
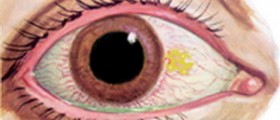
Swollen under eye may appear as a reaction to certain cosmetic products. In that case, it is not a serious condition. When it is caused by certain internal factors, it is important to eliminate the cause of this condition. Fluid retention is one of the causes of the puffy eyes. Women are prone to the hormonal changes during menstruation, menopause or pregnancy. Due to these changes in the levels of the hormones, the fluid usually retains in the subcutaneous tissues under the eyes, thus causing the swelling.Another cause of the puffy eyes is periorbital cellulitis. It is a severe eye infection marked by the painful and tender swelling under the eyes, which is usually accompanied by fever. Low thyroid or hypothyroidism is also responsible for the occurrence of swollen under eye, since the facial puffiness and swelling under the eyes are some of the warning signs of this thyroid disorder. Eczema, psoriasis and many other skin infections, a swell as various allergies to medication, pollutants or insect bites are also potential causes for the appearance of swollen under bags.
Furthermore, the puffy eyes may appear because of sleeplessness and insomnia, but also because of too much sleeping. Other causes for this condition are crying, excessive consummation of alcohol and drugs, as well as cigarettes. Salty foods and a direct injury to the eye are also the causes of the puffy eyes.
- Allergic contact dermatitis of the eyelids should be treated with low-dose topical steroids for five to 10 days.
- Eyelid atopic dermatitis should be treated with oral antihistamines; moisturizers; and low-dose, short-term topical corticosteroids. Only low-dose topical corticosteroids should be used on the eyelids to avoid skin atrophy.
- First-line treatment of blepharitis consists of eyelid hygiene and systemic tetracyclines in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction.
- Mild preseptal cellulitis in older children and adults often can be treated on an outpatient basis with broad-spectrum oral antibiotics and close follow-up. Treatment of orbital cellulitis requires ophthalmology consultation, hospital observation, and broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics.
- Treatment of ocular rosacea includes oral tetracyclines and topical metronidazole (Metrogel) or azelaic acid gel (Finacea).













Your thoughts on this
Loading...