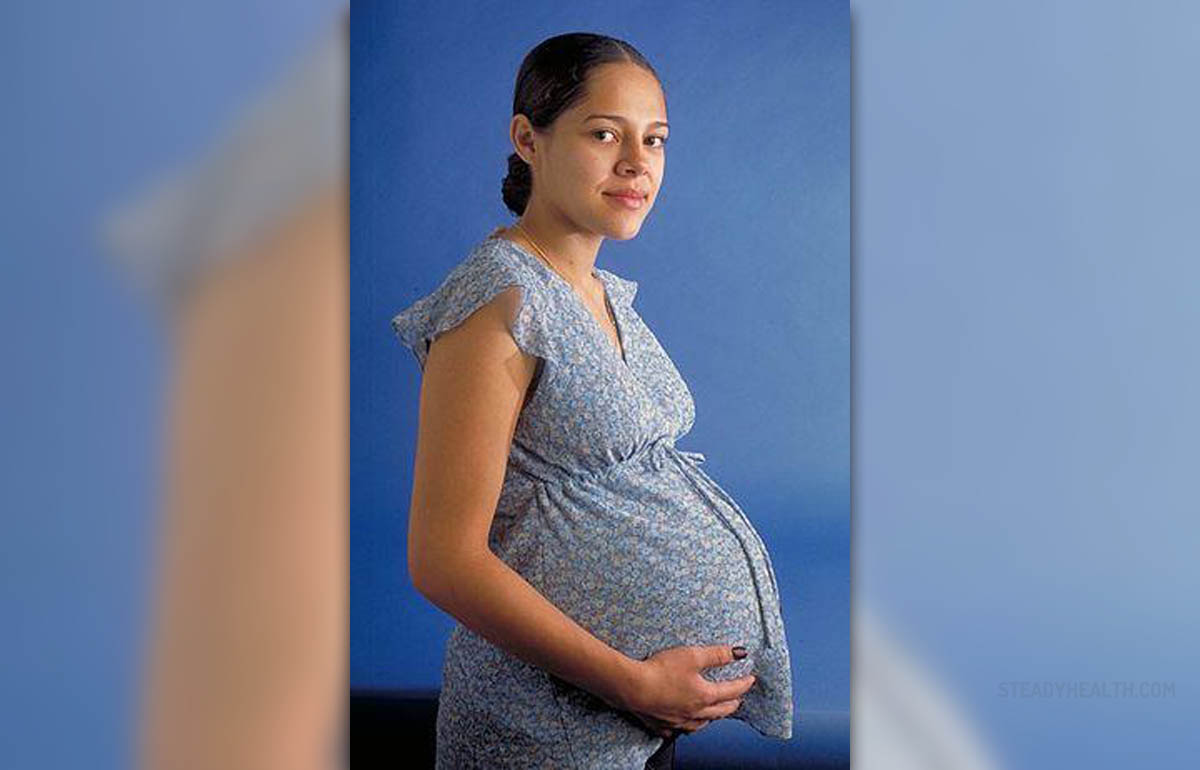

Uterine fibroids are benign growths that consist of cells that are normally found in the uterus. They generally affect women in their reproductive years and are in many cases harmless. These growths practically never undergo malignant transformations. This is a good thing and a woman needs not to worry whether they will one day turn into cancer.
However, they may interfere in the process of implantation and causes various complications during pregnancy. This is the reason why women with certain types of uterine fibroids require special care while being pregnant and those who want to get pregnant and have fibroids should discuss available treatment options prior to conceiving.Regular Control in Pregnancy
All pregnant women undergo routine pelvic exams and ultrasound examination. Together with confirming the pregnancy the doctor may also confirm the presence of uterine fibroids which might have been asymptomatic and caused no problems before the very pregnancy.
It is essential to understand that not all uterine fibroids are harmful to the baby and may cause complications during pregnancy. So being familiar with the types of these benign growths may put mothers-to-be at ease and free them from worry.
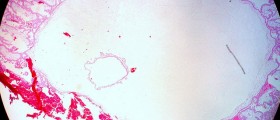
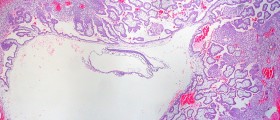
All fibroids of this type are classified into intramural, subserosal and submucosal fibroids. Intramural uterine fibroids grow inside the wall of the uterus and actually represent the most common type of these benign tumors. Subserosal uterine fibroids are located under the outer surface of the uterus i.e. they protrude into the pelvis. They may remain connected to the uterus on a large base or separate from the organ staying connected only via a stalk. Finally, there are submucosal uterine fibroids, the ones that grow inside the cavity of the organ. These fibroids are actually the most problematic because their presence inside the cavity may jeopardize the entire pregnancy especially if they grow together with the fetus.
So, the type of uterine fibroids plays the most significant role in potential complications. The size matter as well but only in case of submucosal fibroids, the ones growing inside the uterine cavity. As for symptoms these tumors may trigger during pregnancy, these most commonly include pelvic pain and light spotting. Fibroids growing on the stalk may undergo torsion. In such case pain becomes unbearable and a woman must undergo surgery straight away.
Tumors located inside the uterine cavity are blamed for miscarriage and may also initiate premature birth. Furthermore, a woman may experience postpartum bleeding, obstructed labor (if the fibroid is located in the birth canal), fetal malpresentation and stalled labor. Such fibroids are frequently a reason why pregnant women eventually undergo cesarean section.Steps when Uterine Fibroids are Diagnosed
It is essential to diagnose uterine fibroid prior to pregnancy. This way the doctor will have insight in their location, size and may monitor their potential growth and opt for surgery if necessary. However, not all fibroids are diagnosed prior to pregnancy. In certain number of women these benign growths are confirmed to exist once the ultrasound exam is performed in order to confirm the pregnancy.
After a woman is confirmed with fibroids further steps depend whether the woman is pregnant or not and according to characteristics of fibroids. Their type, size, number and many additional factors are all taken into consideration when creating a treatment plan.Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
During pregnancy women suffering from fibroids are practically spared from any available treatment option. the doctor will monitor the growth of the tumors and be sure to notice any introductory sign of potential complications. Many times pain in the lower abdomen caused by fibroids may go away if a woman stays in bed and rests for a while. Severe pain as well as profuse bleeding are serious health issues and they both require immediate treatment.
After pregnancy, uterine fibroids may reduce in size spontaneously. However, if they remain the same size and cause certain problems for a long period of time, patients are recommended one of the several available treatments.
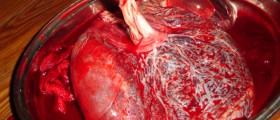
Since uterine fibroids simply do not respond to medications of any type patients routinely undergo surgery in order to get rid of these benign growths. There are several surgical procedures available These include ablation of fibroids, myomectomy and hysterectomy. The first two procedures include only the removal of the fibroids while the uterus remains practically intact. This allows a woman to conceive and have more children. In case of hysterectomy the entire uterus is removed. These women lose the ability to conceive and have children. So, if a woman is planning to have more kids, she is recommended one of the surgeries that will preserve the uterus. Older women and those with severe symptoms of fibroids inevitably undergo hysterectomy.
There is one more treatment option called edocoagulation. This approach is experimental and includes insertion of needle probes directly into the fibroid, cauterization of the tumor and the nearby blood vessels. Due to lack of blood supply, fibroids stop growing and eventually shrink in size and even disappear.
Finally, even though fibroids may be surgically removed, a woman may still develop a new tumor within the period of the following 10 years.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...