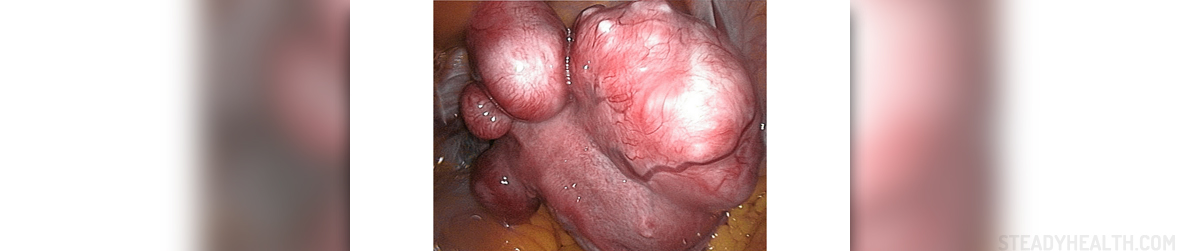
Uterine fibroids, or leiomyomata, are benign muscle growths inside or outside the uterus that develop when uterus muscle cells abnormally grow. This growth results in formation of tumor.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are common condition which can be seen in many women but they rarely cause problems since they are frequently small. Often, they are not even noticed. Causes of uterine fibroids are still unexplained but it has been observed that development of the fibroids is related to hormone estrogen. Uterine fibroids do not grow before puberty. They most commonly start growing after age of 30 and may shrink or even regress when estrogen levels are reduced, after menopause. Due to increased levels of estrogen, uterine fibroids often develop during pregnancy but disappear after delivery. Uterine fibroids are more frequently seen in women who have had the first period before age of 10. Also, women who take oral contraceptive pills rarely develop large uterine fibroids. On the other hand, women that have family history of uterine fibroids have increased risk of developing these growths. Uterine fibroids are two to three times more often seen in African-American women than in white women. African-American women also usually have more symptoms caused by the fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids Types
Types of uterine fibroids are classified by their location in the uterus. Myometrial (intramutal) fibroids are located within the muscular wall of the uterus. Submucosal fibroids are located in the uterine cavity below the lining of the uterus. Subserosal fibroids are commonly located underneath the lining membrane on the outside of the uterus. Pedunculated fibroids are usually found outside of the uterus connected to the organ by a stalk or base. Uterine fibroids may vary in size and may range from microscopic to several inches and weigh ten or more pounds.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
In most cases women with uterine fibroids do not experience symptoms but the condition can cause several symptoms. They include:
Prolonged periods Heavy periods Painful periods Pelvic pain Constipation Bloating or feeling of fullnessSometimes uterine fibroids can affect fertility and pregnancy.
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids can be treated in many ways. Surgery effectively treats the condition but it can be avoided since there are other ways available. They include:
Fibroid Diet – inadequate diet can increase estrogen levels and lead to development of fibroids Systematic enzyme therapy – helps to shrink the fibroids Uterine artery embolization – procedure involves injecting polyvinyl alcohol into the artery that feeds fibroid, leading to the symptom relief and reduction in size of the fibroids Controlling weight – Excess weight can lead to hormonal imbalance and elevated estrogen levels












Your thoughts on this
Loading...