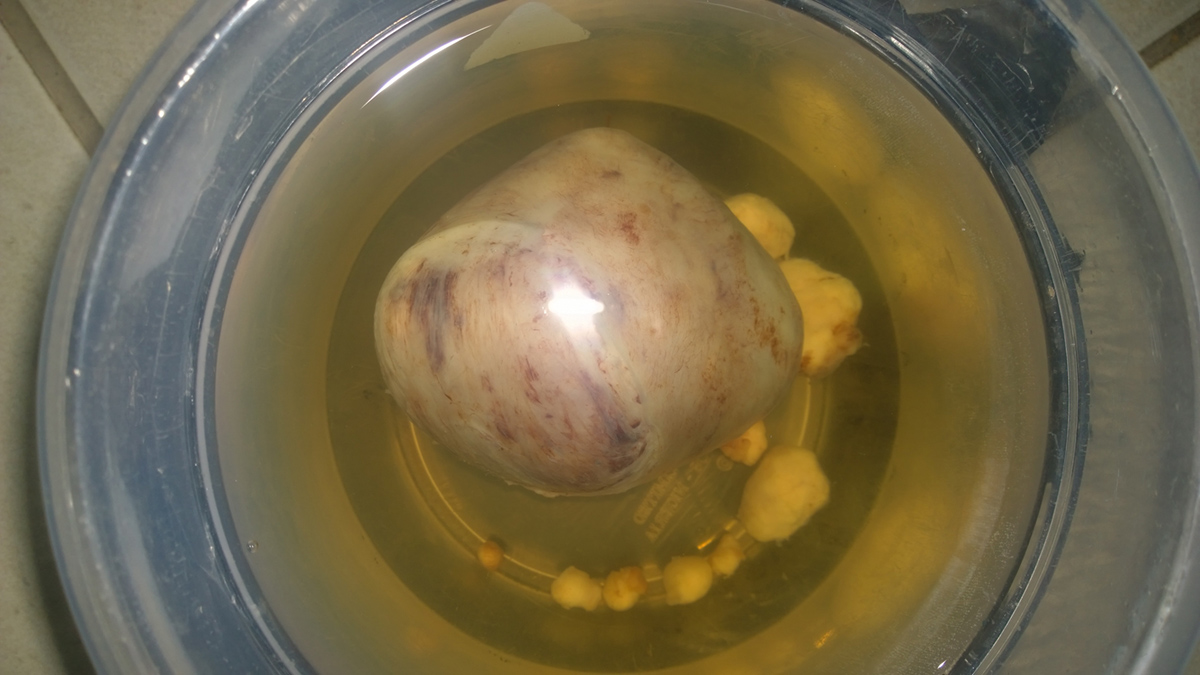

Definition
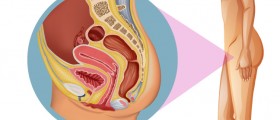
Fibroids are the most frequent benign tumors of the uterus, built mostly in smooth muscles. Basic features of this condition are tumor, bleeding, pain and pressure on surrounding organs and structures. Benign nature of fibroids exclude the possibility of metastasis and spreading to other organs but causes problems because of its location in the uterus (infertility, difficulty in childbirth, miscarriage) and the pressure of the surrounding organs.Cause
The cause of fibroids is not known. Researches shows that fibroid occur with proliferation of altered smooth muscle cells. Estrogen does not cause the occurrence of fibroid, but accelerate its growth.Symptoms
Fibroids may cause symptoms 35% of cases. Fibroids without symptoms reveal themselves accidentally during gynecological examination. Symptomatic fibroids are characterized by a different intensity depending on the size of fibroids, their location in the uterus changes in fibroids and whether a woman is pregnant or not.Symptoms include the following: irregular and profuse bleeding from the uterus that results in anemia, which is usually difficult to treat pain tension in the lower abdomen that occurs due to pressure from fibroids of the surrounding organs and structures. If the tumor is large, it can cause venous delays and thrombosis, and bowel discharge disordersinfertility (2-10% of infertility is due to fibroids) miscarriages - occurs twice more frequently in women with symptoms of fibroids
Diagnosis
For the diagnosis of fibroids a detailed interview with a patient is required, which includes providing information about current symptoms, as well as about previously present illness, family illness, functions and habits.This is followed by gynecological examination which can be supplemented with digitorectal examination (examination of the last part of the colon). Also ultrasound examination is desirable.
Complications
Benign changes in the fibroids are usually degenerative such as dying of fibroid cells, accumulation of fat it them appearing cysts or disposal of calcium. They may be swollen, or bleed. Fibroid infection is common after these changes. Fibroids deform uterus and press ovaries and fallopian tubes facilitating infertility.Malignant change in fibroid is very rare, occurring in only 0.1 to 0.5% of cases.
Treatment
Fibroid treatment depends on several factors - the age of the women, the number of deliveries, whether she is currently pregnant or desires pregnancy the fibroid symptoms the location of the tumor general health of the patient and the existence of possible complications in the tumor or other organs.Little fibroid without complications and symptoms can be treated with hormone therapy - gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa). By this treatment achieves reduction of tumor in about half of the patients, which is often a sufficient therapeutic effect. The effect of this treatment means reducing the concentration of female sex hormone - estrogen, which can also lead to unwanted symptoms such that in postmenopausal women. Effect of reduction by using GnRHa is unfortunately, only temporary. It is used if a woman wants to have more children if for whatever reason can not conduct the surgery for fibroid removal and in preparation uterus for surgery.
Large fibroid, which causes symptoms and develops complications, is recommended to remove by surgical treatment. Fibroid can be removed by myomectomy or by removing the entire uterus - hysterectomy which depends on the woman's desire for more children and other factors. Tumor in pregnancy is a particular problem and need a good estimate of the potential consequences of surgery such as miscarriage or premature labor.
Fibroids in postmenopausal women, or just before it if they don’t cause symptoms or complications, shouldn’t be operated. In postmenopausal women, the estrogen effect disappears slowing or even stopping fibroids growth.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...