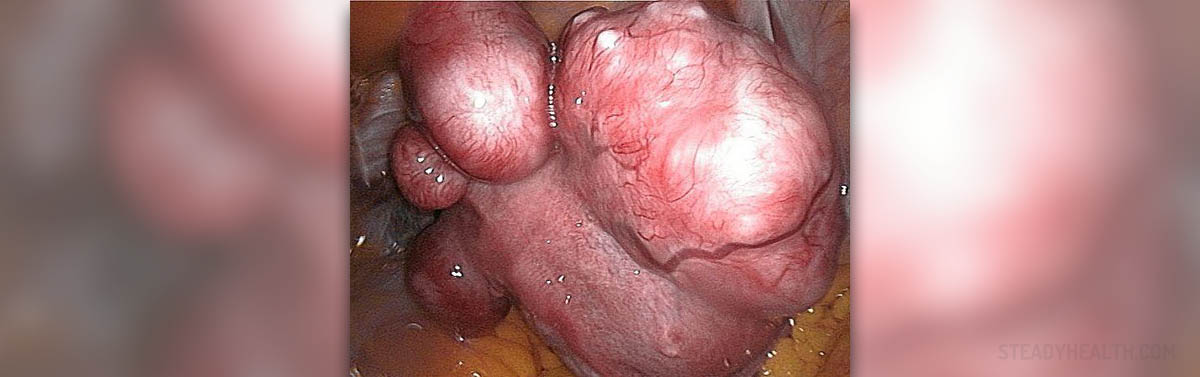
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that originate from the smooth muscle layer and connective tissues of uterus. Tumor is a synonym for a neoplasm that is formed by an abnormal growth of neoplastic cells. Tumors are often confused with cancers but, in fact, only small portion of tumors is cancerous. Cancer is malignant by the rule, while tumors may be benign, pre-malignant, malignant, or may not have any cancerous potential. Uterine fibroids are the most common benign tumors in women. They usually appear in the middle and late reproductive years. It is estimated that about ¾ of all women have uterine fibroids at some point in their lives. For most of them, these benign tumors have no symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids
As already stated, for many women, uterine fibroids do not cause any kind of serious troubles. Very often, women are completely unaware that they are having a tumor inside of their uterus. Uterine fibroids may be entirely asymptomatic, especially when they are small in size. However, some women may feel symptoms of this condition, but it generally depends on the location of the tumor and on its size. Heavy periods, abnormal bleeding from the vagina, abdominal discomfort or bloating, painful defecation, pain in the back, pain during the sexual intercourse, or even problems with fertility, are all associated with uterine fibroids.
Causes of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids, like any other kind of tumor, form as a single cell continues to reproduce repeatedly. This way, the cell grows into a rubbery mass that is different from the rest of the tissue. Sometimes, these lesions are very small and almost invisible by the human eye. However, fibroid tumors can be very large and cause a lot of discomfort to the patient. Some women may have only one tumor; while the others may have numerous fibroid tumors that may expand all over the uterus and even reaches the rib cage.
The exact causes of uterine fibroid tumors are not clear. Scientists believe that a number of different factors may decide if a woman is going to get a uterine tumor or not. For example, certain fibroid tumors are apparently linked with certain alterations in genes that are responsible for uterine muscle cells.
Hormones, especially estrogen and progesterone, are known to stimulate development of uterine lining. Uterine fibroids contain more estrogen than normal uterine muscle cells, and this is where the possible link exists. Other factors may include insulin-like growth factor and other body chemicals.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...