Introduction to Fibroid Tumors
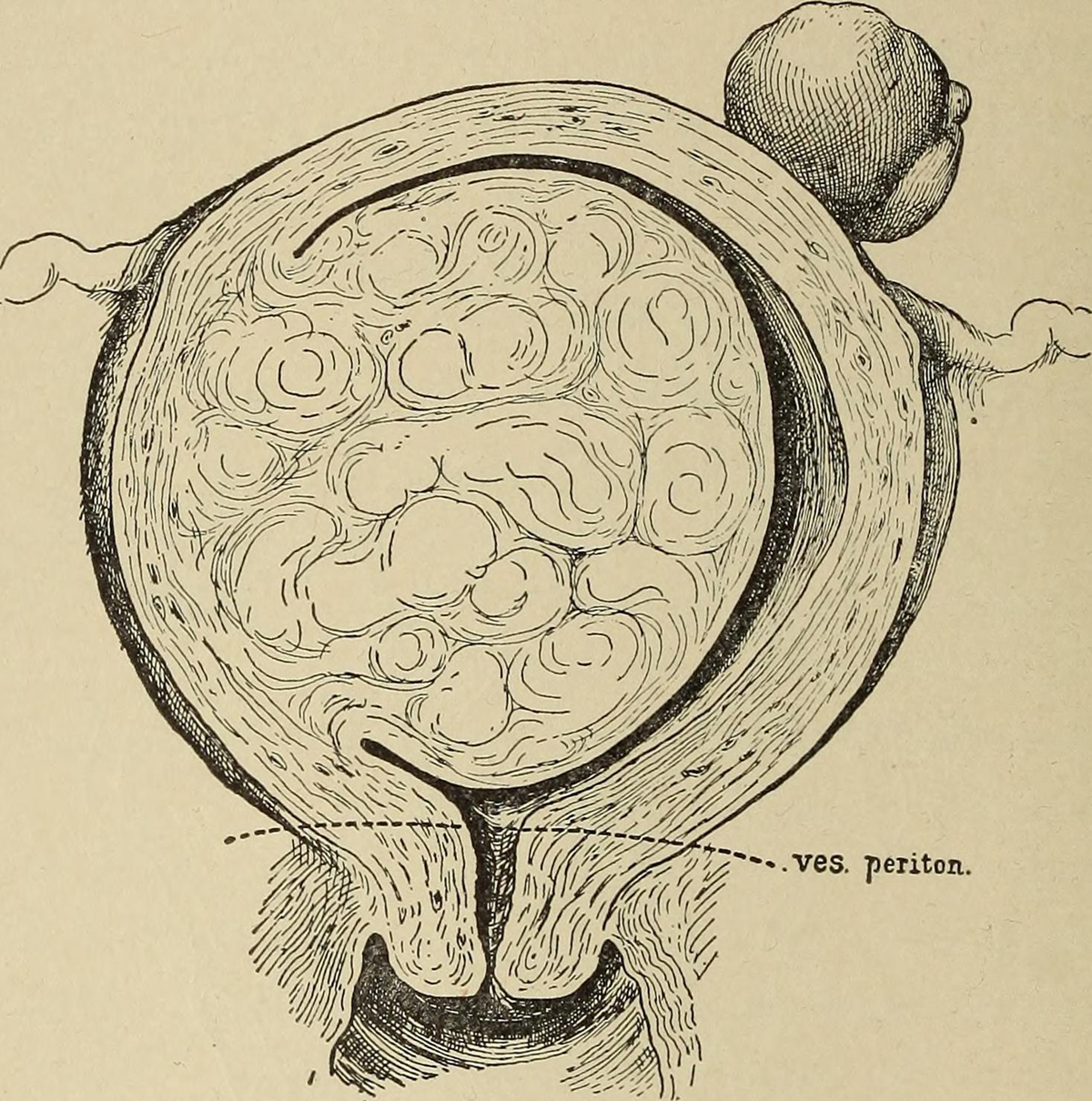
Fibroid tumors are benign tumors of the uterus and they are commonly found in women in their 30s and 40s. These tumors are made of fibrous tissue and can be solitary or present in a large number. Fibroid tumors grow slowly and usually cause no symptoms.
The actual cause of fibroid tumors has not been fully understood yet. Such tumors can develop once the body starts to produce estrogen. They also grow until there is a sufficient amount of estrogen. In case of increase of estrogen (pregnancy) fibroid tumors can rapidly increase in size while it is common for them to shrink during menopause (lack of estrogen). This drives to conclusion that estrogen has something to do with fibroid tumors.
All fibroid tumors are classified into submucous, intramural and subserous fibroid tumors. Submucous fibroid tumors cause bleeding between the periods and may induce severe cramping. Intramural fibroid tumors are located in the wall of the uterus and usually do not cause any problems at all unless they grow to a significant size. And finally, there are subserous fibroid tumors. They are only treated in case they drastically increase in size and start to cause certain problems.
Treatment for Fibroid Tumors
There are several treatment options for fibroid tumors and they include monitoring, pharmaceutical therapy, artery embolisation and surgical fibroid tumor treatment. Which of these treatment modalities is going to be applied depends on the nature of the tumor, its type, size and number.
In some women fibroid tumors are only monitored and they are only treated in case they grow rapidly or reach certain size and start to cause problems. This particularly refers to intramural and subserosal fibroid tumors. Such tumors can be efficiently monitored with thr occasional pelvic ultrasound.
Pharmaceutical fibroid tumor therapy includes administration of birth control pills. Some patients may be also treated with GnRh agonists which effectively reduce production of estrogen in ovaries and may reduce the size of fibroid tumors.
Uterine artery embolisation is a non-surgical procedure. It is performed by a well experienced interventional radiologist. The specific substance is injected via a small catheter that is inserted into the femoral artery. The goal of the therapy is to block the blood flow to the tumor, cease its growth and this eventually leads to tumor shrinking.
Surgical fibroid tumor treatment includes myomectomy and hysterectomy. In myomectomy the surgeon removes only the tumor while hysterectomy includes surgical removal of the entire uterus. After myomectory a woman preserves her child bearing capability while after hysterectomy a woman cannot have children any more.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...