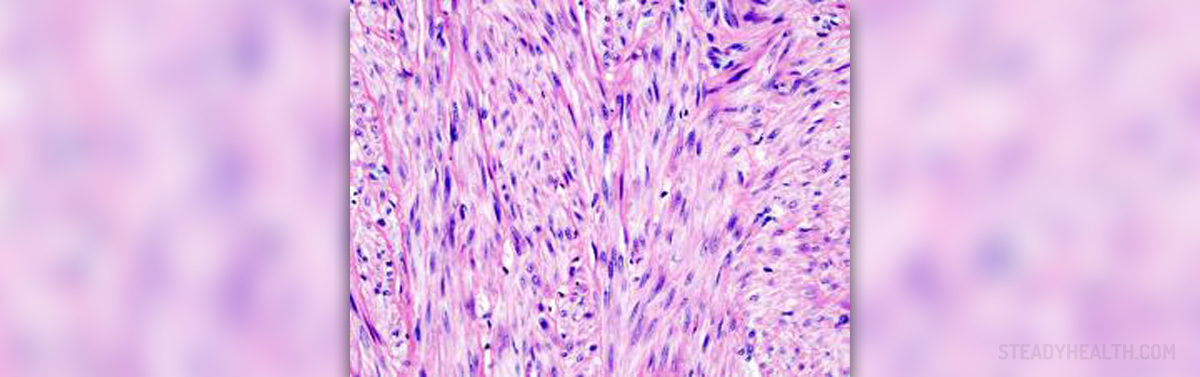
A fibroid tumor is a benign growth made of smooth muscle cells and fibrous tissue. This tumor most commonly affects women and develops in the uterus. It is a firm, rubbery tumor usually of spherical shape. The size of fibroid tumors varies a lot and they may be rather small (1mm in size) or grow up to 20 cm.
These benign tumors commonly affect women in their reproductive age. According to data 20-40% of all women between the age of 30 and 50 are susceptible to fibroid tumors. There is a connection between increased levels of estrogen and fibroid tumor occurrence. Fibroid tumors may develop outside the wall of the uterus. These are known as subserosal fibroid tumors. Furthermore, they may occur in the very wall of the uterus and then they are classified as intramural fibroid rumors. And finally, if they are localized under the inner lining of the uterus wall, fibroid tumors are classified as submucosal fibroid tumors.
Symptoms and Signs of Fibroid Tumors
The actual size of fibroid tumors as well as their localization determines the intensity of the symptoms.
One of the leading signs of fibroid tumors is heavy blood loss which typically affects menstrual period. The periods may last longer than 5 days and apart from heavy bleeding the patients may also complain about intensive pain. The previously mentioned is commonly associated with the presence of intramural or submucosal fibroid tumors. Furthermore, abnormal uterine bleeding such as clots in the blood or irregular patterns during period may be additional signs of fibroid tumors.
The growth of the tumor may affect the nearby pelvis organs. Namely, the tumor may compress certain nerves and cause pain. Additionally, if large enough the tumors may compress the very bladder or the rectum and lead to increased urge to urinate or defecate. And in some cases the pressure caused by fibroid tumors may eventually stimulate pain in the legs.
Women suffering from submucosal or intramural uterine fibroids may have difficulties in getting pregnant and the presence of these types of tumors during pregnancy may cause miscarriage or premature birth.
And finally, if these tumors are small in size they are usually discovered accidentally during a routine pelvis examination and pelvis ultrasonography.
Treatment for Fibroid Tumors
The treatment for fibroid tumors depends on several factors. They include the location of the tumor, its size and symptoms they cause. In case of small fibroid tumors, especially if they are subserosal, there is no need for treatment. Intramural and submucosal fibroid tumors may be a problem for women who are trying to conceive or who are already pregnant. If these tumors cause serious symptoms and interfere in process of getting pregnant they are surgically removed. Myomectomy is surgical removal of fibroid tumors. In women who are in menopause and in those who do not want to have children any more one more surgical option is hysterectomy, a surgical removal of the entire uterus.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...