A tendon is a thick, elastic cord of connective tissue that connects muscles to bones. It assists in moving bones and joints while muscles are contracting thus enabling us to walk, jump and make any other movements. Tendons can be of different sizes and shapes. Healthy tendons move smoothly while muscles contract.
However, although they are very strong, tendons can get damaged due to overstrain or an injury. Impaired function of a tendon can cause inflammation and painful movement resulting in tendonitis.
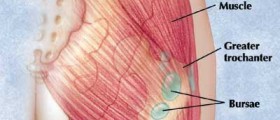
Tendonitis CausesTendonitis may affect any tendon in the body. However, tendons around the shoulders, elbows, wrists and heels are most commonly affected. This is because these tendons have a “watershed zone”, an area with weakest blood supply which makes them prone to damage. Such tendons also have poor healing response because of body’s difficulty in distributing oxygen and nutrients required for healing of a tendon.
Tendonitis usually develops over time due to repetitive motions or sudden injury. Overuse of tendons is common in people whose jobs or hobbies involve repetitive motions such as gardeners, painters, tennis players, golf players and baseball players.
People aged between 40 and 60 are prone to tendonitis and with age tendons lose their elasticity and become weaker. Obesity, anatomical abnormalities and underlying conditions can also cause tendonitis.
Tendonitis SymptomsTendonitis causes the following symptoms:
Pain triggered by movement of muscles and tendons Tenderness Swelling Stiffness in the affected joint and limited motionDiagnosis and Treatment for Tendonitis
Tendonitis can be confirmed with the help of physical examination, medical history, x-rays and MRI. X-rays and MRI are not necessary for diagnosis tendonitis but are used to rule out fractures and other problems that may cause pain and swelling.
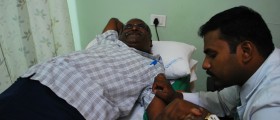
Treatment for tendonitis aims to relieve the symptoms. Over the counter pain relievers, ice packs and rest are recommended to reduce pain and swelling. Also, the affected person must avoid activities that aggravate the problem. If tendonitis does not improve in a couple of days, it can be treated with corticosteroid injections administered into the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy is also used to increase range of motion. Surgery is needed in rare cases when other treatment options fail. People with chronic tendonitis are advised to protect the affected tendon while doing certain activities.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...