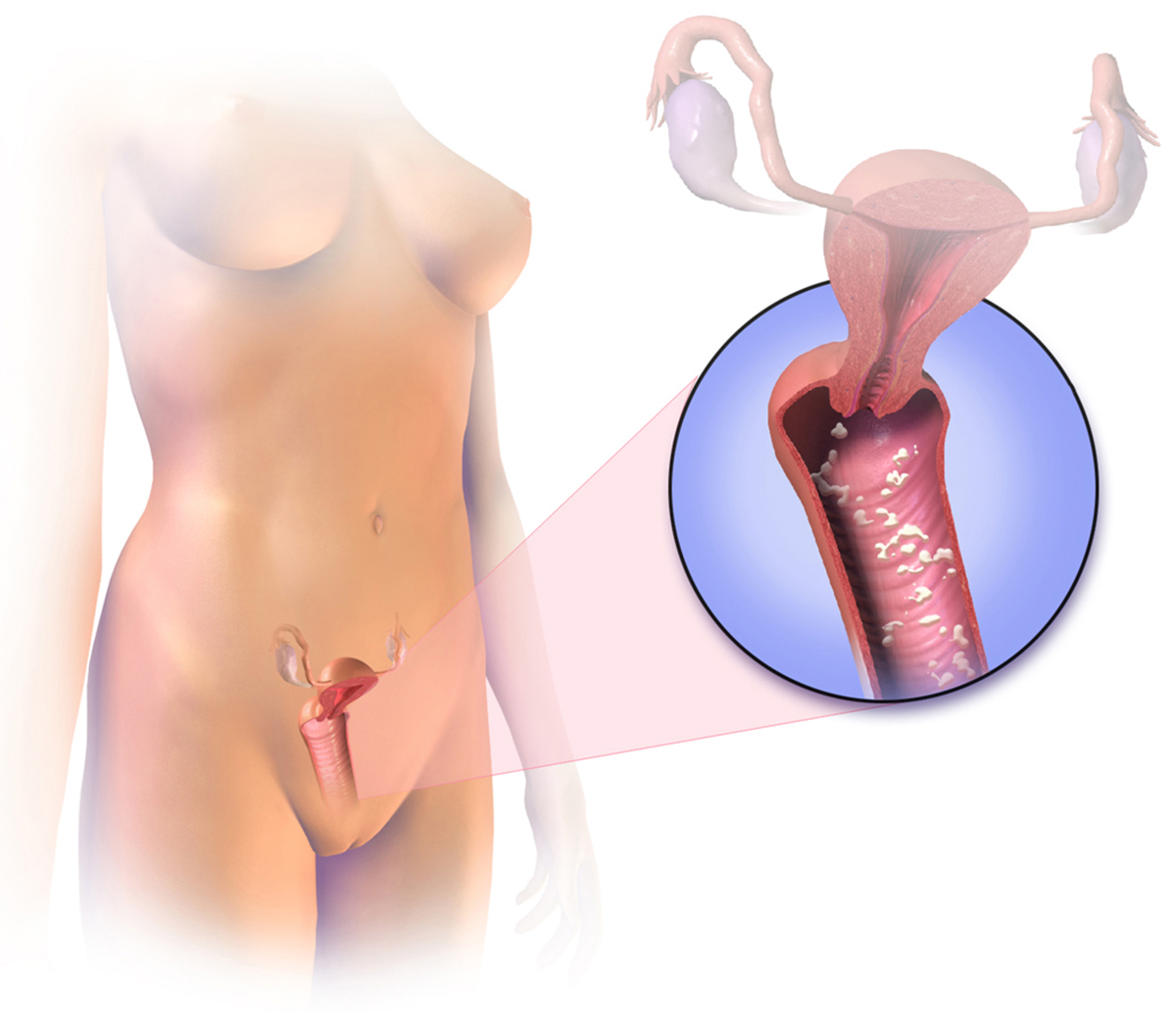
Yeast is a fungus normally found in healthy skin and moist areas on the body like the mouth and vagina and in cases of fungi overgrowth these areas become infected. Yeast infections are most commonly caused by Candida albicans, which is the type of fungus, and these infections are not referred to as sexually transmitted disease since the yeast has already been present in the vagina and sexually inactive women can be infected just as well. Still, men can experience irritation on the penis after sexual contact with the infected partner. A woman can suspect she has a yeast infection if she experiences an itching or burning sensation around the vagina (this can also happen during urination) if the pain or discomfort occurs in the vagina during sexual intercourse; or if the vaginal discharge resembles cottage cheese (in some cases it is thinner or it may not appear atall). Still the same symptoms can be present in the cases of some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or other inflammations so it is important to see a doctor to rule out these more serious conditions.
It is estimated that 1 in 20 women will suffer from a recurrent yeast infection, which should certainly be reported to the doctor. Other situations that call for a visit to the doctor’s office include pelvic pain, fever and a colored or fowl smelling discharge experienced by pregnant or breast-feeding women, children under the age of 12, diabetics or persons with the weakened immune system. Vaginal yeast infections can occur when the new yeast enters the vaginal area or when there is the overgrowth of the yeast already present which can happen as a result of the use of antibiotics or immunosuppressants. Women that have suffered injuries to the inner vagina especially after chemotherapy are also prone to yeast infections while other risk groups includes women in using oral contraceptives, pregnant women, women with suppressed immune system or those using douches or scented vaginal sprays.
Oral and topical antifungal medication is available for the treatment of vaginal yeast infection, but if yeast is accompanied by another microbe, combination of treatments is required. Topical creams used to treat the yeast infection include Terazol, Monistat, Lotrimin and Femstat 3, whereas Lotrimin, Mycelex, Monistat, Terazol and Mycostatin are available in vaginal tablet form. Doctors usually opt for the vaginal treatment with vaginal tablets or suppositories. Oral medication is not recommended to pregnant women since it can cause nausea, headaches or abdominal pain, but vaginal medication does not cause these side effects.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...