Any person suffering from internal hemorrhoids wants to find the best treatment to relieve unpleasant symptoms. In this article, we will provide information on several treatment options for internal hemorrhoids.
What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are dilated or bulging veins of the rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids that originate at the top of the anal canal are called internal hemorrhoids, while hemorrhoids formed near the anus are known as external hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids do not cause pain unless they have prolapsed, but anal itching and bleeding while passing stool are common symptoms of internal hemorrhoids.
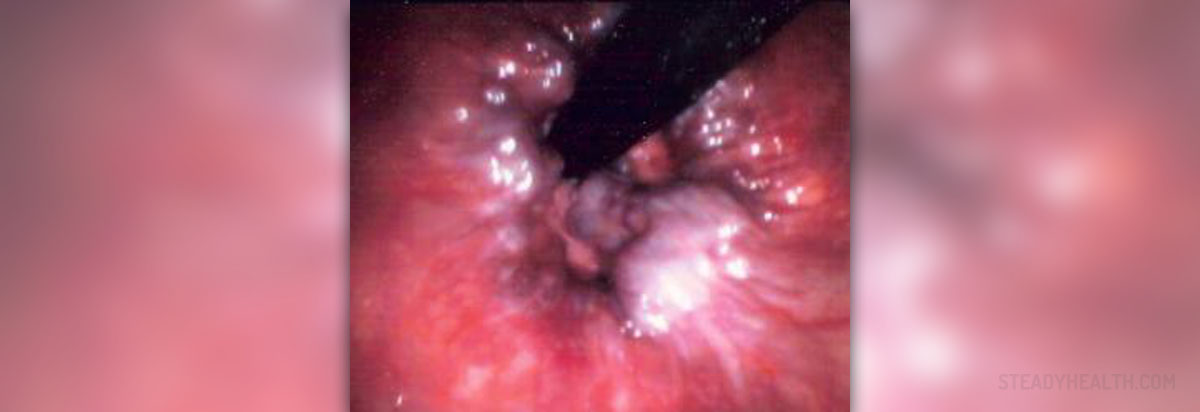
They can occur due to several reasons. Pregnant women often develop hemorrhoids. Constipation is a common cause of hemorrhoids too. Other causes of internal hemorrhoids include a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged sitting, a low-fiber diet, anal or rectal infection, and anal intercourse. Frequent use of laxatives and obesity can also contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
In order to treat the condition one must identify the exact cause of hemorrhoids. There is no treatment that can cure hemorrhoids but there are several treatment options that can help to manage the condition and relieve the symptoms.
Natural treatments for internal hemorrhoids include increasing the fiber in a diet or use of supplements to help in regulating bowel movement by softening stool and reducing strain while defecating. There are also various over-the-counter products in the form of ointments, gels, creams, suppositories, foams, and pads that help relieve internal hemorrhoid symptoms.
Surgical treatment is needed only in case of severe internal hemorrhoids.
Treatment for Internal Hemorrhoids
The following are non-operative and surgical treatments for internal hemorrhoids:
Rubber Band Ligation
In this procedure, a small rubber band is placed at the base of hemorrhoid in order to cut off blood flow through the affected area. This causes hemorrhoids to shrink and fall off within four to seven days after the procedure.
Laser Coagulation
Laser coagulation uses a laser device to apply an electric current to the hemorrhoids. This triggers a chemical reaction in the hemorrhoids, which interrupts the blood supply and result in their shrinking.
Injection Sclerotherapy
This method involves the injection of a chemical solution into the mucus membrane near hemorrhoid. This chemical solution acts by preventing blood flow to the affected area, which results in the shrinking of hemorrhoids.
Infrared Photocoagulation
This treatment method involves directing an infrared beam that kills tissue surrounding hemorrhoids and causes scar tissue to form. This causes hemorrhoids to shrink.
Hemorrhoidectomy
This is a surgical removal of hemorrhoids. It can be performed with a scalpel, cautery device, or laser. This treatment is used in third or fourth-degree hemorrhoids that do not respond to other treatment options.
- People with hemorrhoids, and those wrongly thought to have hemorrhoids, had a tendency to use self-medication rather than to seek proper medical attention. According to the Google’s annual roundup in 2012 (Google Zeitgeist), hemorrhoids was the top trending health issue in the United State, ahead of gastroesophageal reflux disease and sexually transmitted disease.
- Treatment options mainly depend on the type and severity of hemorrhoids, the patient’s preference, and the expertise of physicians. Low-graded internal hemorrhoids are effectively treated with dietary and lifestyle modification, medical treatment and/or office-based procedures such as rubber band ligation and sclerotherapy.
- A meta-analysis of 7 clinical trials comprising of 378 patients with hemorrhoids showed that fiber supplement had a consistent benefit of relieving symptoms and minimizing risk of bleeding by approximately 50%.
- There are several modern drugs and traditional medicine used which are available in a variety of format including pill, suppository, cream and wipes. However, the published literature lacks strong evidence supporting the true efficacy of topical treatment for symptomatic hemorrhoids. For an oral preparation, flavonoids are the most common phlebotonic agent used for treating hemorrhoids.
- Many office-based procedures (such as rubber band ligation, injection sclerotherapy, infrared coagulation, cryotherapy, radiofrequency ablation and laser therapy) are effectively performed for grade?I- II hemorrhoids and some cases of grade III hemorrhoids with or without local anesthesia.
- Vacuum suction ligator may offer clearer visualisation of hemorrhoids and more precise placement of banding when compared to a traditional forcep ligator.
- Surgical intervention is usually required in low-graded hemorrhoids refractory to non-surgical treatment, high-graded symptomatic hemorrhoids, and hemorrhoids with complication such as strangulation and thrombosis. An operation for hemorrhoids may be performed if patient has other concomitant anorectal conditions requiring surgery, or due to patient’s preference.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...