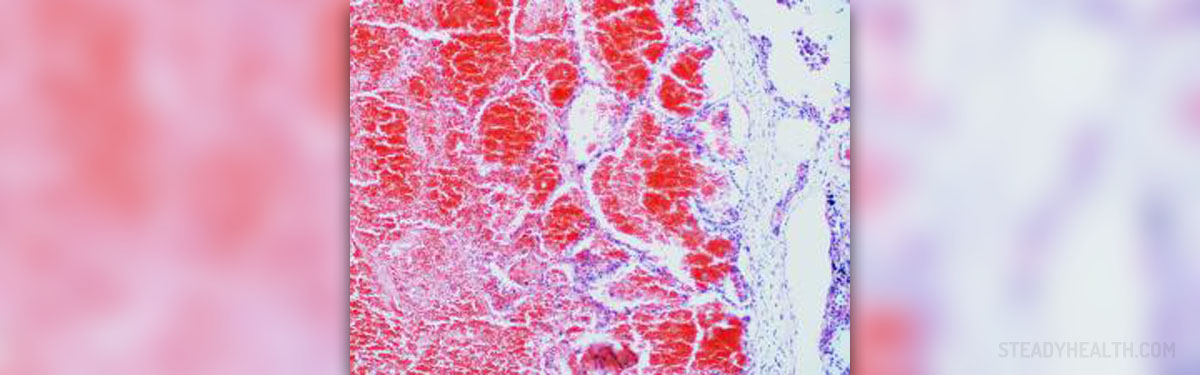
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding in the brain caused by the rupture of certain blood vessels. The bleeding, either minor or major, can cause serious damage to the brain and its structures. Apart from direct damage, bleeding causes brain swelling and leads to increase in intracranial pressure causing even more damage.
Hemorrhagic stroke commonly occurs due to increased blood pressure and prior damage of the blood vessels. The most susceptible blood vessels are those affected by atherosclerosis and those with aneurysms. Increased risk of bleeding is also evident in elderly people who are suffering from accumulation of amyloid in arteries. Brain tumors can additionally lead to serious brain hemorrhage. And finally, people with arterial-venous malformations are prone to hemorrhagic stroke more than healthy people.
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke occur unexpectedly and develop rather quickly. They include general weakness, numbness of certain body parts and loss of sensation, loss of coordination, partial or total ipsilateral loss of vision, speech difficulties, headache, lightheadedness, vertigo, problems with swallowing, inability of the patient to recognize/ identify well-known things. In severe hemorrhagic stroke, patients are sleepy and lethargic and in most extreme cases they lose consciousness and coma occurs.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhagic Stroke
The doctor performs neurological test which points to certain abnormalities. The patients are confused and sleepy. The most significant test in conformation of brain hemorrhage is CT scan of the head. The diagnosis can be also set after MRI of the head.
Treatment for Hemorrhagic Stroke
The goal of the treatment is to take care of symptoms, stop the bleeding and prevent complications. Essential part of the treatment is rehabilitation which starts rather soon. Recovery is gradual and may be complete or incomplete.
The treatment right after the stroke has been diagnosed, includes prompt hospitalization. Patients are in an intensive care unit. They are monitored for potential complications. Some of the patients need to be intubated and those who cannot breath on their own require the assistance from mechanical ventilation.
Medications are given to bring increased pressure under control and antiedematous therapy reduces the pressure inside the skull. Patients who have developed seizures are given anticonvulsants. Bed rest is crucial for all the patients since it prevents repeated intracranial hypertension. Stool softeners can help with bowel movements and prevent elevation of pressure during defecation.
The recovery can be complete. Still apart from medications patients need to undergo physical therapy, speech therapy and occupational therapy or additional interventions depending of the severity of the stroke.
In certain cases patients require operation which may save their lives and improve chances of further recovery. Surgery is performed in all cases when bleeding can be stopped. Surgery is also performed to treat some of the complications of hemorrhagic stroke such as hydrocephalus.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...