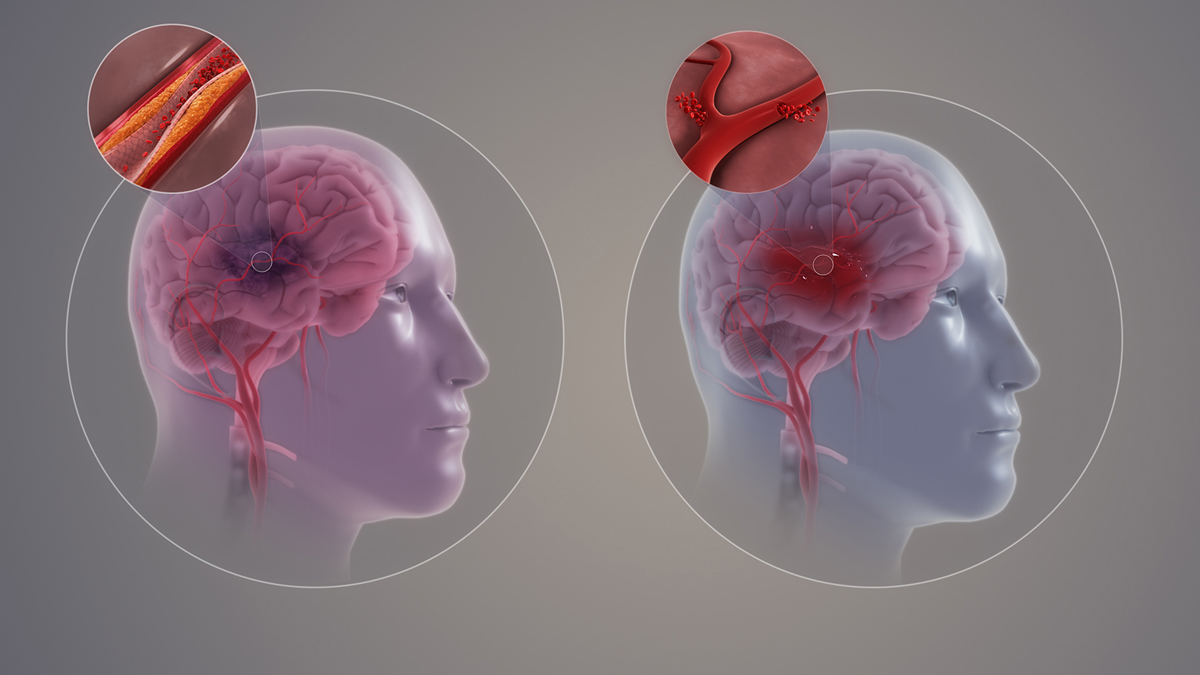
A stroke is rather serious condition that results as a consequence of improper blood supply to the brain. The brain is an organ which needs oxygen and glucose to function properly. Any cut in supply even minor may lead to serious and permanent damage to the brain cells. The cells that have died cannot be replaced as the brain cannot regenerate. Therefore the prevention of the stroke is the best cure as once it has occurred it can lead to serious complications and permanent damage of the affected parts. In worst cases of the stroke the lethal outcome is almost inevitable.
The stroke can be caused by ischemia (insufficiency in blood supply due to clots) or by hemorrhage. Apart from these fully developed forms of stroke there is a sort of pre-stroke condition classified as TIA or transient ischemic attack. In TIA blood supply is momentarily interrupted but re-established again. Transitory ischemic attacks have to be taken seriously as they almost always present an introduction to full stroke.
Symptoms of the stroke need to be recognized instantly and one should be immediately transferred into hospital. Obvious symptoms of stroke include paralysis which mainly affects one side of the face. The paralysis may affect arms and in severe cases the whole half of the body can become paralyzed. One may complain about difficulties with walking or problems in keeping balance. Abrupt changes in vision may be additional sign of the stroke (double vision, loss of visual field and so on). The speech is slurred and increased production of saliva with improper swallowing lead to drooling. One may be confused to speak incoherently and lose sense of space and time. A severe headache usually develops before the stroke.
Apart from general symptoms additional ones may be present. They mostly depend on whether the stroke has been caused by bleeding or blood clotting. They can also differ according to the localization of the stroke.
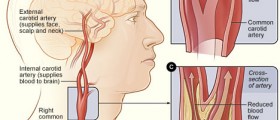
The stroke induced by ischemia affects the opposite side of the body comparing to the side of the brain that has been affected by the very stroke. If bleeding was the cause of the stroke the symptoms are additionally enhanced by increase of intracranial pressure. The symptoms of increased intracranial pressure include severe headache, vomiting, seizures and loss of consciousness. In this case one may even end in coma.
Stroke usually develops quickly. However sometimes symptoms increase gradually over the minutes, hours or even days. This is connected to the size of the affected blood vessel.








-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...