A stroke is a serious and life-threatening medical condition which features with rapid loss of brain functions due to insufficient blood supply of brain tissue. Oxygen and sugar are two essential nutrients for brain tissue. Oxygen is very important for the brain and needs to be administered continuously. The lack of oxygen causes damage to the brain tissue which may be reversible or irreversible depending on how long the shortage of oxygen lasts.
What Happens During a Stroke
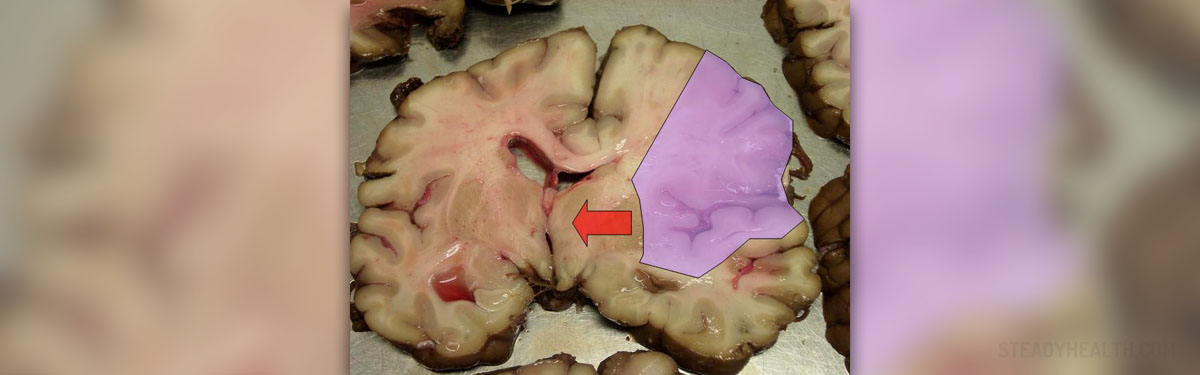
There are two types of stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. In ischemic form of the disease the blood supply with oxygen to the brain is significantly reduced and in hemorrhagic stroke there is bleeding into the brain.
Permanent damage to the brain cells occurs if there is a lack of oxygen supply which lasts more than 4 minutes. Since the brain needs the oxygen a several mechanisms try to compensate for inappropriate blood supply. This includes enlargement of the blood vessels near the affected area. Unfortunately, if the blood supply is not restored the affected part of the brain permanently loses its functions.
The loss of function in stroke can be permanent or temporary and it also varies in intensity. This depends on which artery has been affected, how long the brain has been deprived from oxygen and whether the process of blood flow restoration has been successful.
Symptoms of Stroke
The characteristic symptoms and signs of stroke include sudden weakness and numbness of ipsilateral parts of the body or even one entire half of the body, intensive headache, sudden dizziness, blurred vision, slurred speech, loss of balance and disorientation and in severe cases of stroke the patients may lose consciousness and end up in a coma.
Effects of Stroke
After the stroke the recovery time may take up for months and some people with severe damage of the brain function never re-establishe the lost brain functions. Stroke may lead to serious disability and patients may end bedridden for the rest of their lives.
One of the sequelae is permanent weakness of muscles and/or paralysis which causes difficulty in walking and coordination. Furthermore, after a stroke patients may face cognitive difficulties such as memory loss and problems in logical thinking. There is also chance of emotional changes, especially depression. Patients may be irritable, confused, angry and frustrated. If speech centers have been damaged the person have problems with speech and language. In severe cases there may be swallowing difficulties which is a major risk factor for choking. And finally, in some cases of stroke patients remain bedridden, they are not able to function on their own and require permanent supportive care and attention.






-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...