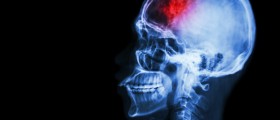
A mini-stroke refers to a transient ischemic attack (TIA) — a temporary interruption of blood flow to part of the brain.
Ischemia
The brain needs constant delivery of oxygen and blood to supply around 100 billion neurons. Normally, blood circulates across numerous blood vessels to reach every part of the brain. However, blood vessels may become narrowed or blocked by blood clots or cholesterol plaque so that a part of the brain does not get enough oxygen and nutrient-rich blood. The resulting condition, when brain areas starve and finally stop functioning, is known as ischemia.
Mini-stroke
A mini-stroke is a brief period of blood flow interruption in the brain. Patient suffering a transient ischemic attack shows symptoms of brain function injury: difficulty to speak or move limbs on one side of the body. Symptoms may usually last from a couple of minutes to a couple of hours, but they usually go away within a day. Sufferers from mini-stroke are at higher risk of having a major stroke within three months. Up to 20% of patients may have this problem consequently. Mini-strokes are signs that a debilitating stroke is on the way and it is of crucial importance to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms are sudden and they may vary from patient to patient depending on the portion of the brain that is affected. Symptoms may be extremely mild or even unnoticeable if the stroke affects areas that are used minimally in day-to-day function. Extremely disturbing symptoms will show, if the stroke affects vital areas of the brain.
Most commonly affected areas of the brain are those that control motion and feeling in the face, arm or leg. This may sometimes lead to problems in understanding and producing speech. Most common symptoms are weakness or numbness of the face, limbs or muscles on one side of the body; inability to speak or understand spoken language; unexplained dizziness or vertigo; loss of vision through one eye; double or blurry vision.
The difference between a mini-stroke and a stroke
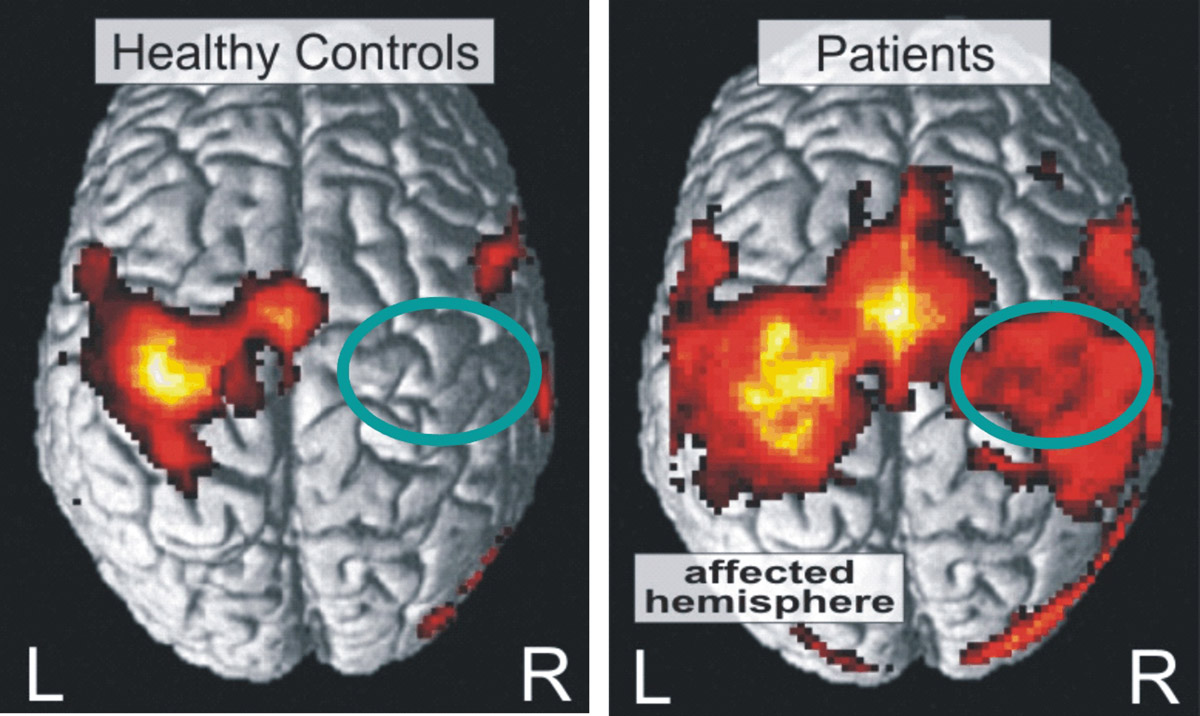
The main difference is that symptoms of mini-stroke withdraw completely within 24 hours. Strokes leave long-lasting physical complications. However, MRI examinations of brain of patients who suffered mini-stroke and patients who suffered stroke shows no difference. The reason for this is yet unknown, but it is a subject of scientific studies. An assumption follows from this: mini-strokes may also cause permanent damage to the brain, no matter their symptoms last only for a small amount of time.








-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...