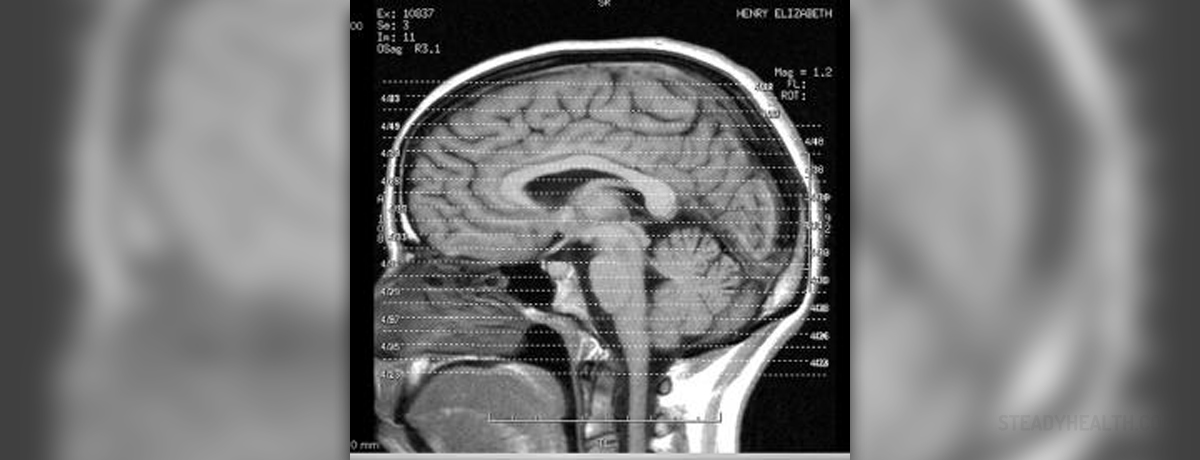
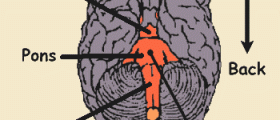
The brain stem is the posterior part of the brain. It is structurally continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. This portion of the brain is very important for many bodily functions.
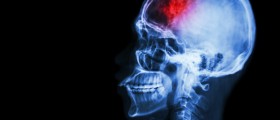
A stroke which takes place inside the brain stem is classified as brain stem stroke. Since this part of the brain contains vital centers (centers that regulate heart action and breathing) a brain stem stroke in many cases leads to lethal outcome. Only if the treatment starts on time and if there is no significant damage to the brain stem a patient may survive.
Causes of Brain Stem Stroke
Brain stem stroke occurs as the consequence of blocking of the blood vessels that supply this part of the brain with blood. Brain stem blood vessels are basically already structurally damaged (atherosclerosis) and the blockage of the blood supply develops as the consequence of blood clots. Furthermore, even bleeding from the blood vessels may cause damage to the brain stem. Since brain cells simply cannot survive without oxygen in case blood flow is not restored soon enough the affected cells become necrotic and lose their function for good.
Symptoms of Brain Stem Stroke
The most common symptoms of brain stem stroke are dizziness and slurred speech. In case of severe stroke there are serious breathing difficulties.
Some patients develop paralysis. Paralysis is either partial or complete and it can be temporary or linger for the rest of the patient's life.
Coma is one more feature of brain stem stroke. It develops as a consequence of impaired breathing and heart rate. Some patients recover from coma while in others the illness progresses and leads to lethal outcome.
And finally, two more potential symptoms of brain stem stroke are ataxia and nystagmus.
Treatment for Brain Stem Stroke
The goal of the treatment for brain stem stroke is to restore normal blood flow through the blood vessels that have been blocked. The recovery depends on the intensity of the damage to the brain stem. Furthermore, if vital centers inside the brainstem have been deprived of blood supply the patient may die.
Apart from medicamentous therapy all the lost bodily functions may be restored up to a certain extent or completely with physical therapy. In extreme cases of brain stem stroke patients may require support form a ventilator. This is not a good prognostic sign. It is clear that brain stem stroke (as well as any other stoke) represents a serious medical condition which carries many potential complications and sequelae. This is why it is best to prevent a stroke form occurring rather than dealing with it.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...