Stroke-Overview
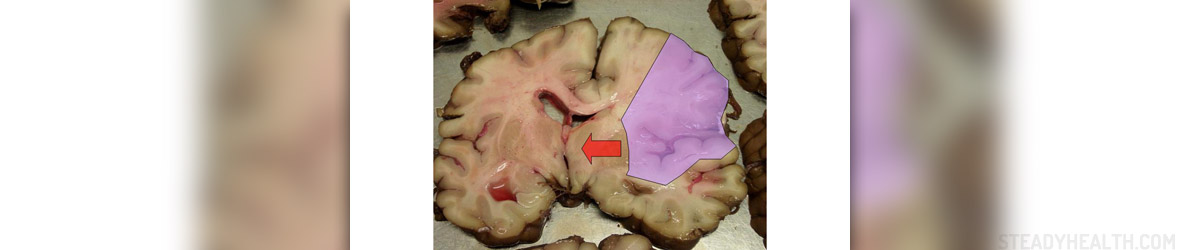
Also known as cerebrovascular accident, a stroke is brain damage that occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or gravely reduced. This means that the brain cells are getting no oxygen and food, and they begin to die out within minutes. A stroke is classified as medical emergency as it can cause permanent neurological damage, severe complications, and even death.
There are two types of strokes: ischemic stroke (the more common kind, caused by a blood clot that blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain) and hemorrhagic stroke (caused by a blood vessel that breaks for some reason and bleeds into the brain). There are also “mini-strokes”, or transient ischemic attacks, that happen when the blood supply to the brain is momentarily interrupted.
Risk Factors
There are certain risk factors that might considerably increase one’s chances of having a stroke. These are: genetics (if someone from a person’s family has had a stroke or a heart attack, they also might have a stroke), a sedentary lifestyle, high cholesterol (which blocks the arteries), high blood pressure, excessive drinking, smoking (and even being regularly exposed to second-hand smoke), cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, drug abuse, being overweight or obese, etc.
The only way a person might prevent a stroke is by leading a healthy life-style. This is achieved by eating plenty of fruit and vegetables, avoiding drinking and smoking, exercising regularly, not using drugs, and maintaining a healthy weight, etc.
Also, people with high cholesterol, diabetes and high blood pressure should consult the doctor on how to control their condition in the best way.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a stroke are: trouble with walking, speaking and understanding, trouble with seeing, sudden shooting headaches, paralysis or numbness on one side of the body or face.
It is vital that, should one feel these symptoms or see anyone experience these symptoms, someone call an emergency number. Every minute counts, and there should be no delay in calling theparamedics.
Treatment
The initial treatment of the stroke depends on whether a person is experiencing an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. In case of the ischemic stroke, the doctors will try to restore the blood flow to the brain. Also, measures will be taken to stabilize a person’s vital signs, including giving them medicines (such as Aspirin, or tissue plasminogen activator, etc.).
In the case of the hemorrhagic stroke, the doctors will try to control and stop the bleeding, and reduce the pressure in the brain. Once the bleeding stops, the treatment usually involves bed rest and supportive medical care while the body absorbs the blood. Medicines may be given to control blood pressure, brain swelling and seizures. Also, surgical measures may need to be taken to repair the blood vessel that was bleeding and relieve the pressure.
After the patient’s state has stabilized, rehabilitation might be needed. Early aggressive rehabilitation allows a person to regain some normal functioning. The rehabilitation will be based on the physical abilities that were lost, the general health of the person before the stroke, and one’s ability to participate.






-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...