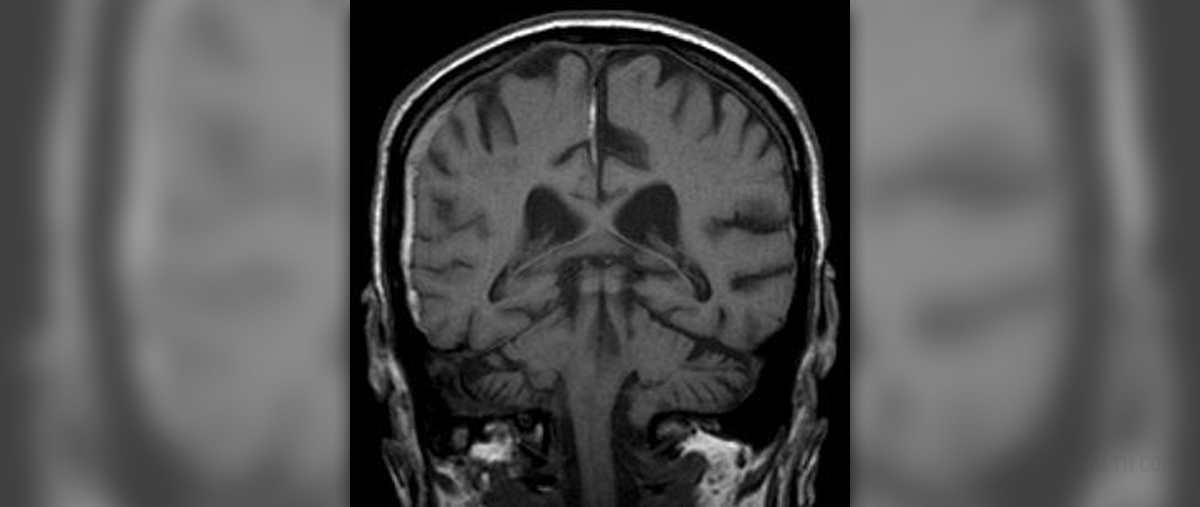
Subdural hematoma is a type of hematoma that develops due to accumulation of blood within the outermost meningeal layer. Blood accumulates between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater as a result of injury and rupture of certain blood vessels (the blood vessels which cross the subdural space). The condition can be acute or chronic and in both cases it requires proper treatment.
Causes of Subdural Hematoma
In majority of cases subdural hematoma develops due to a severe brain injury. While acute subdural hematoma occurs due to heavy and rapid bleeding from the injured blood vessels, chronic subdural hematoma develops gradually because the bleeding is in this case minor and lasts for longer period of time. Acute subdural hematoma is a life-threatening medical condition which, if not treated, leads to lethal outcome.
Subdural hematomas may also occur in case of minor head injuries, particularly in elderly people. Minor head injuries are most commonly responsible for chronic subdural hematomas.
Apart from injuries subdural hematomas also occur spontaneously and the risk of such bleeding is increased in patients on anticoagulant therapy, long-term alcoholics and people with recurrent falls and head injuries.
Symptoms of Subdural Hematoma
Depending on the severity of bleeding symptoms and signs of subdural hematoma develop within minutes or are delayed and occur after a couple of weeks. Heavy bleeding is always a cause of increased intracranial pressure and there can be damage to different parts of the brain. Severe hemorrhage is always accompanied by some neurological deficits.
Many patients have a combination of different symptoms and signs. These may include fluctuating levels of consciousness or even loss of consciousness, disorientation, amnesia, headache, irritability, seizures, numbness and dizziness. Additional symptoms and signs include weakness or lethargy, personality changes, inability to speak or slurred speech, difficulty walking, hearing loss and blurred vision. Increased intracranial pressure results in vomiting and in severe forms there are altered breathing patterns. Diagnosis and Treatment for Subdural Hematoma
In order to set correct diagnosis doctors perform physical as well as neurological exam. A medial history of head injury is also an important fact. Subarachnoid bleeding is easily confirmed with the assistance of CT scan or MRI of the head.
Since subdural hematoma represents an emergency condition, patients undergo emergency surgery which reduces the pressure inside the brain. By drilling a hole in patient's skull the doctor allows the collected blood to drain. However, in case of large hematomas patients must undergo craniotomy. Swelling of the brain is reduced with corticosteroids and diuretics while seizures require adequate anticonvulsants.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...