Anal fissures are common with people of all ages, younger or healthy people, no matter.
Hemorrhoids can develop anal fissures. What is an anal fissure? It’s a damage of lining of the lower rectum also known as anus is an anal fissure. This tear causes pain due to a bowel movement. The condition is pretty common and harmless because anal fissures are not serious medical conditions.
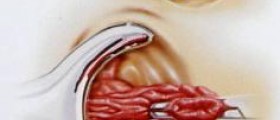
Anal fissures can be at home in a period of days or months, and are called acute anal fissures. If it isn’t cured in period of six weeks, it becomes a long-term chronic condition. There are medicines to cure chronic anal fissure. And there are surgeries only for fissures that are not treatable with medicines.

Causes of Anal Fissure
There are cases when the anal fissures can be caused by Crohn's disease. It is a disease of inflamed bowel (IBD), and causes diarrhea with blood, abdominal pain, weight loss, fever and fissures around anus area. Childbirth can make a fissured anal canal. Also; anal intercourse, an examination that uses digital insertion, insertion of objects.
Diarrhea is common no matter of anal fissures; anal fissures can be caused by other things. It is possible to have an excessive tension in between two muscular rings that are controlling anus. Human conscious controls the external anal sphincter, but the internal anal sphincter is not willingly controlled. This muscle is pressured, or under the tension non stop, therefore a fissure might happen if internal sphincter's pressure becomes high enough to cause spasm and reduce blood flow of the anus. The pressure may keep a fissure from the healing.
Anal fissures can be created with injury or trauma of the anal canal. Those injuries are more than we think. For instance, an injury can cause by repeated diarrhea, constipation (a hard stool) or a mechanical stretch of the anal canal.
Signs and Symptoms of Anal Fissure
Clear symptoms of anal fissures are burning pain, itching and stinging sensation due to a movement of a bowel. The pain due to a fissured anal canal can be severe and long lasting and can bleed lightly, with a yellowish discharge stool. Bleeding separately from the stool is also possible. Fissures can create very dark, dark red bloody and tarry painful stools. This condition might be an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or even colon cancer. Anal fissure do not have to be painful but bleeds occasionally.
Diagnosis
According to symptoms diagnosing is quite possible, also anus examination. The fissure is easy visible if doctor spreads back side cheeks with fingers.
The examination of anus can be done with digital rectal examination or using anoscope instrument that can review a fissure closely. In case of extremely painful fissure, it is necessary to wait to a certain level of healing, before doing a rectal exam anoscope check. In very painful cases it the option to use a topical anaesthetic.
It is also necessary to judge if the fissure causes ill condition of the patient. In case of several fissures located around or in anus there are other conditions to be considered, conditions such as syphilis, infection, tuberculosis, inflammatory bowel disease, HIV, a suppressed immune system or anal cancer.
Treatments
Acute fissures can be treated at home. One of the ways is taking laxatives, increasing fiber in daily food intake and having a bath in a shallow tub of warm water 2 or 3 times a day. Even if pain goes away, fissure needs time to heal in total. Some fissures can heal with no treatment. Constipation or hard stool slows a fissure healing process.
- This retrospective study involves 110 consecutive female patients, all affected by idiopathic and non-recurrent CAF who underwent a surgical procedure, from January 2010 to January 2019. Exclusion criteria for the study were: the presence of multiple fissures, fistulas in ano, syphilis, inflammatory bowel disease, anal abscess, malignant disease and previous anorectal surgery. All patients were followed up for at least 2 years after the surgical procedure. The patients’ outcome data were retrieved from a prospectively monitored database.
- At 12 and 24 months after surgery maximum resting pressure (MRP) and maximum squeeze pressure (MSP) values were substantially unmodified in the patients with normotonic internal anal sphincter (IAS). In those patients with hypertonic IAS MSP values were immodified as compared to the values at 12 and 24 months after surgery; whereas MRP ones were significantly lower at 12 months follow-up as compared to the pre-operative ones but still significantly higher than those measured in healthy controls. At 24 months follow up after surgery MRP values were within normal range.
- We recorded 15 cases of pre-operative FI (13.63%), in 7 of them CAF was located at the anterior commissure (18.42%), in 8 of them at the posterior one (11.11%).
- At 24 months after the surgical procedure follow-up we recorded 8 recurrences (7.3%). In 6 of them MRP values were normal and they were successfully treated with conservative therapy (pharmacological and hygienic-dietary approach). In 2 cases there was a mild hypertonic IAS, these latter have been treated with dilatation with complete healing.
- The results of this study show that fissurectomy and anoplasty associated with a pharmacological therapy in case of hypertonic IAS is feasible and effective; this procedure allows a perfect post-operatory faecal continence and a low rate of recurrence.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...