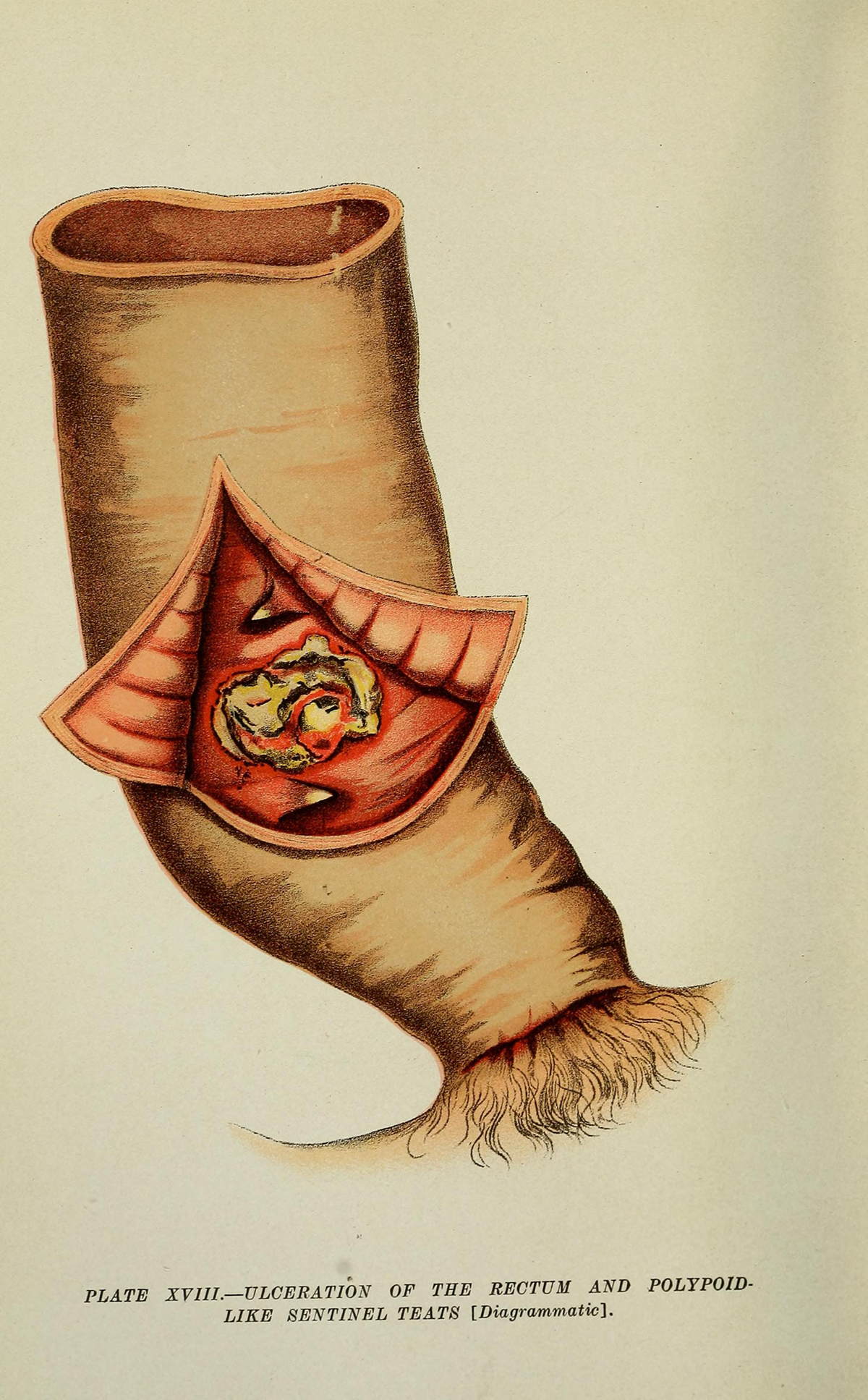
Anal fissures represent small tears (splits) affecting the mucous membrane of the anus. They develop in the distal part of the anal canal and are initially limited to the epithelium. These tears may after some time, particularly if not treated, affect even deeper structures and spread to the full thickness of the anal mucosa.
It is estimated that anal fissures affect both genders equally. The condition is, however, more common in younger individuals as well as middle-aged people.
Anal Fissure Etiology
Scientists have not managed to reveal the mystery regarding the underlying cause of the condition. Still, what they know is that anal fissure develops after the affected area has been somehow traumatized. Namely, trauma to the anal canal is most commonly associated with passing hard stool and constipation. Trauma of this kind is common in people whose diet does not include sufficient amount of fiber available in many fruits and vegetables.
Furthermore, people who have undergone some surgical procedures in the affected area may be more prone to anal fissure because the previously cut tissue is now more susceptible to trauma induced by hard stool.
It is normal to experience tears in the anal mucosa if there is constipation and one suffers from hard stool issues. In majority of people such tears soon heal without any long-term sequelae. However, patients in whom there are abnormalities of the internal sphincter of the anus or abnormalities of the very anal canal may experience inadequate healing of such tears.
Hypertonicity as well as hypertrophy of the internal anal sphincter are abnormalities that cause increased pressure inside the anal canal and also contribute to an increase in the resting sphincter pressure. Majority of patients with anal fissures are actually suffering from an elevated resting pressure. This abnormality can be easily dealt with surgical sphincterotomy.
The posterior anal commissure is an anatomical part of the anal canal frequently inadequately supplied with blood. So, if this area is additionally hypertrophic, blood deprivation becomes even more prominent, inducing higher level of ischemia. Lack of blood supply is thought to be a major contributor to inadequate healing of many anal fissures.Anal Fissure Clinical Characteristics
Symptoms and signs of anal fissures are characteristic. This is why doctors can diagnose the condition after taking medical history alone while with physical examination and examination of the affected area the diagnosis is only confirmed.
Patients generally report constipation and pain during bowel movement. Such pain is recurrent and always induced by defecation. This is why patients experience fear of defecation. Additionally, people may notice the presence of bright red blood on the toilet paper and stool. Bleeding is extremely in a form of a few blood drops that may end up in the toilet bowl. There is no profuse bleeding and significant blood loss.
If acute anal fissures do not heal properly, the condition becomes chronic. In such case doctors can easily notice the fibers of the internal anal sphincter in the base of the chronic opening. There is also an enlarged skin tag located distally to the anal fissure.
Patients are initially treated conservatively. Surgery is reserved for anal fissures that do not respond to medical therapy. Finally, chronic fissures can be only dealt with surgically.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...