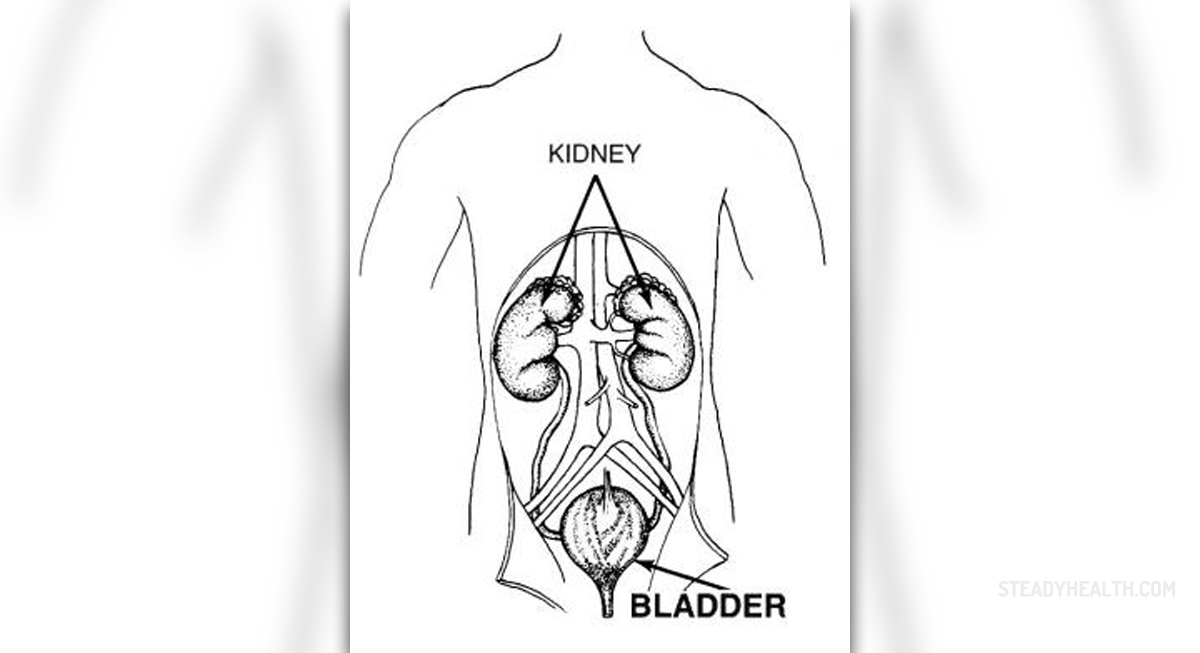
Bladder is an organ which is a part of the urinary tract in the human beings. Its main role is to store the urine that comes from the kidneys through the ureters till the time of urination comes. This organ, as well as any other, can be affected by many disorders. One of the bladder disorders is its infection, which is called cystitis. Cystitis is more frequent in women than in men, since the urethra in women is shorter than in men so pathogens can easier reach this organ. In the greatest number of cases, the bacteria that cause bladder infection are Escherichia coli. However, cystitis may also be caused by other bacteria, such as Staphylococcus, Enterobacter, Proteus and Klebsiella.
Causes of bladder infection
Cystitis is usually induced by one of two major causes. In some cases, the bacteria which are present in the vagina get rubbed in the wall of the uterus during a sexual intercourse. From the uterus, the bacteria reach bladder and start to multiply, thus leading to the occurrence of bladder infection.
The bladder is an organ which has the ability to stretch in order to store necessary amounts of urine. When a person frequently holds the urine for a long period of time, the bladder muscles become weak over time. Due to this weakness, the bladder is not capable to eject all the urine from it, and the small amounts stay in the bladder, making a good environment for the overgrowth of bacteria.
Symptoms of bladder infection
When bladder infection occurs, it manifests through several signs and symptoms. The most common symptoms of cystitis are constant urge for urination, frequent urination and painful urination accompanied by burning sensation. The urine in people who suffer from bladder infection is usually dense and cloudy, and it has foul smelling odor. Sometimes, only small amounts of urine are released.
Hematuria is also a sign of this bladder disorder, and it is the condition marked by the blood in the urine. Other symptoms of cystitis are pelvic pressure, low-grade fever and tenderness in the bladder region, as well as nausea and vomiting. When cystitis occurs in women, they may experience painful sexual intercourse and pain in the lower abdomen.
Bladder infection is diagnosed after careful examination of the symptoms and after the urine test is done. Once it is diagnosed, the doctor prescribes antibiotics for the treatment since antibiotics kill the bacteria in the body.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/cystitis/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000521.htm
- Photo courtesy of Pearson Scott Foresman by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bladder_(PSF).jpg
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...