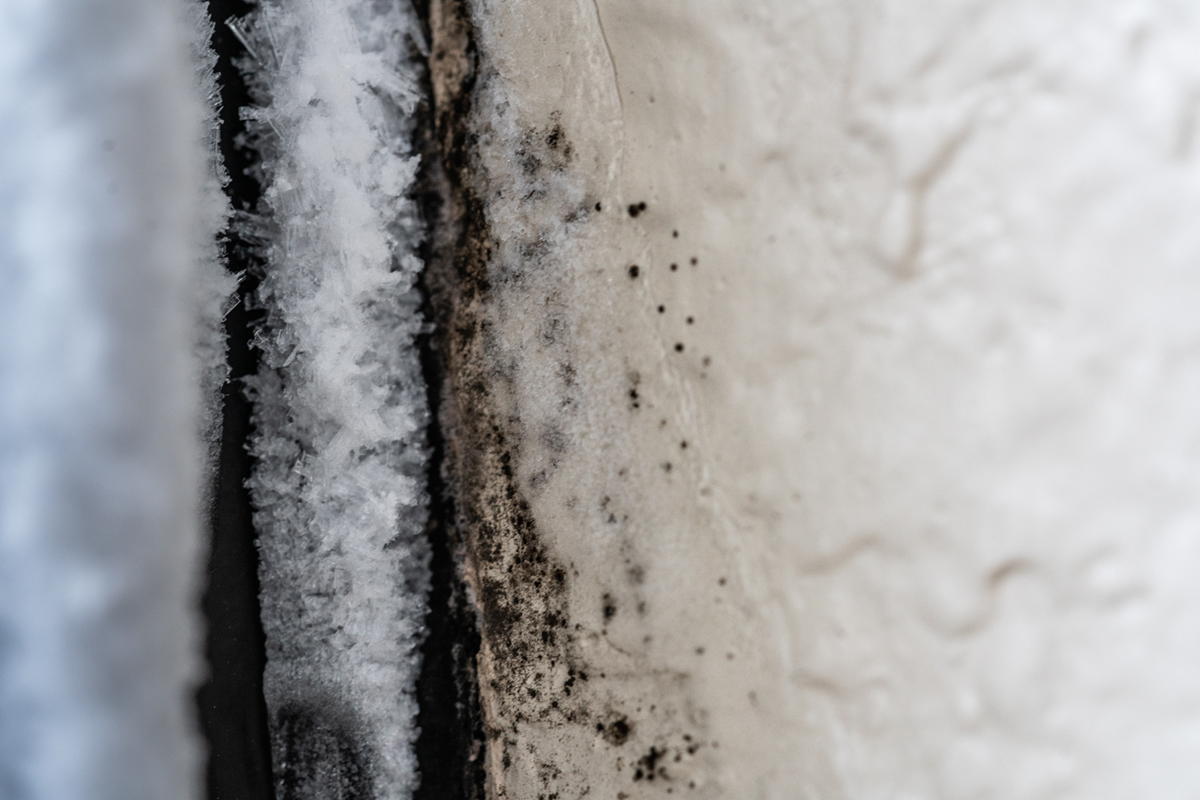

Black mold, or toxic black mold, is a mold of Stachybotrys genus, known as Stachybotrys chatranum. This mold occurs in spaces with poor air quality. The mold arises after fungal growth on water-damaged building materials. Fungi grow and thrive in moist dark places and molds are a subtype of fungi that produce fluffy or powdery growth on surfaces. Toxic black mold can grow almost anywhere when most conditions exist, especially on carbon containing materials. The black mold forms when there is a high humidity level, condensation and water intrusion. In home buildings, this usually happens when there are indoor leaks and floods, or insufficient flow of air.
Health effects of toxic black moldThe black mold produces trichothecene mycotoxins, including satratoxins, a naturally occurring mold byproduct toxic to humans and animals. Exposure to this toxic material can provoke a great variety of adverse responses in humans. The response is highly individual, as the sensitivity of each person may vary drastically. Children, old people and people with compromised immune systems are at a higher risk of experiencing undesirable health effect in contact with black mold. The routes of exposure include ingestion, inhalation and skin contact.People sensitive to black mold usually experience an allergic reaction. The most frequent symptoms of an allergic reaction are a runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, coughing, sneezing and throat irritation. The more serious symptoms are caused by chronic conditions such as sinusitis and asthma, and include symptoms that can be extreme, such as nausea, vomiting, and bleeding in the lungs and nose.
Volatile organic compounds, can irritate mucous membranes and the central nervous system, and produce a whole range of unpleasant symptoms such as headache, low attention span, difficulty to concentrate and dizziness.
In a small number of cases, toxic black mold can cause invasive disease due to the exposure to microorganisms that do not normally produce disease in healthy individuals. People with serious immuno-compromising diseases such as HIV/AIDS, or people on immunosuppressive drugs, are at the highest risk.Epidemiology
It is estimated that nearly all cases of chronic sinus infections, somewhere around 37 million only in the United States, are due to molds. Moreover, an increase of 300% increase in the asthma rate over the past 20 years has been linked to mold. An allergy to mold is very complex as the initial reaction triggers a cascade of reactions that manifest in series of unpleasant symptoms. Even after the exposure has passed, a body still produces antibodies, so that any later contact with the mold causes overreaction of the immune system. However, one can take a number of simple steps to reduce mold growth in the environment, and prevent the recurrence of allergic reaction.



-Does-It-Help-Treat-Allergic-Rhinitis_f_280x120.jpg)








_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...