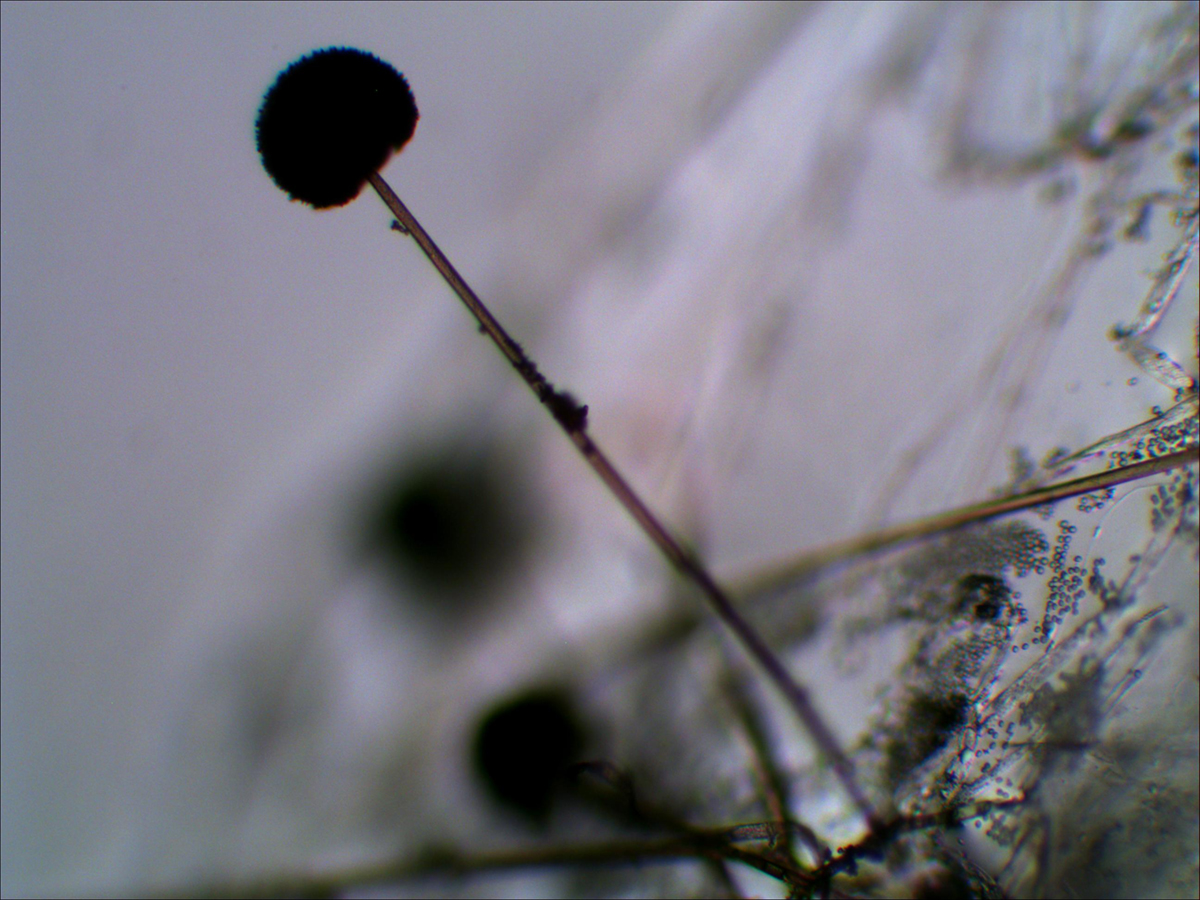
Black Mold
Stachybotrys mold genus contains about 50 different species and is actually a type of fungi. Almost all of these fungi may cause problems for people but some of them are more toxic than others. The most toxic kind of molds for people is Stachybotrys chartarum or Strachybortys atra, also known as black or toxic black mold.
Usually, black mold affects people living in buildings damaged by water, especially wood, ceilings and bathrooms. There are cases that black mold infected cotton clothes and also insulation and dry walls.
- A few threats from inhaled molds have been perceived for a long time. Since the 1890s, outdoor settings in the U.S. Southwest have been linked with coccidioidomycosis, caused by a fungus in the soil.
- By about 25 years ago, there was some initial evidence that damp indoor spaces were linked with health problems such as bronchitis, asthma, cough, wheeze, and shortness of breath.
- Wherever they grow, molds must have some source of water and food. The accumulating evidence has shown that problems with mold can surface anywhere in the world after just one or two days of moisture exposure, in settings wet or dry, hot or cold, north or south.
- Mycotoxins have often been the main point of contention in recent insurance claims and lawsuits over suspected harm from moldy buildings. In the 2004 EPA-funded report Guidance for Clinicians on the Recognition and Management of Health Effects Related to Mold Exposure and Moisture Indoors, researchers at the Center for Indoor Environments and Health at the University of Connecticut Health Center wrote that mycotoxins can elicit responses in almost anyone they come in contact with, that the health effects are worrisome, and that infants, at least, should be removed from suspect settings.
- The substantial increase in air conditioning all over the world is another potential culprit, with more than fifteen studies consistently indicating a strong link with numerous respiratory symptoms. Microbes thriving in air conditioning systems, including fungi and bacteria, likely contribute to that link.
- Given the evidence at hand, Health Canada has determined that mold may pose a health hazard, and on 31 March 2007 released brief recommendations for cleaning up mold in residences. The EPA is developing guidelines for moisture control “best practices” in all phases of design, construction, and maintenance, and may finalize the guidelines in 2008.
There are many health problems connected with the black mold and the severity of this medical condition depends on the kind of mold that infected people. Black mold may have toxic effects on the human body and these should be taken very seriously. These molds are known to produce trichothecene toxins, including mycotoxins, which cause all the damage in human body. Mold spores can be transmitted by air and cause a disease, or people or animals may ingest mycotoxins (mold, fungal toxins) and end up ill.
The fungi might also get transmitted through the cuts and the sores on the human skin. Sometimes, people with immune system impairments are more likely to suffer from black mold infection. This includes people suffering from bronchitis and other respiratory problems, but also cancer and AIDS/HIV patients, who could have extremely difficult medical problems.
Black Mold Health Problems
Any unusual symptom may indicate that you are suffering from black mold poisoning. Patients might notice lung problems such as asthma and bronchitis, or skin problems. There might also be some sinus issues, like cough, headaches, sore throat, tremors, or flushed skin.
Sometimes, black mold toxicity may cause chronic tiredness in both humans and animals. These fungi could also cause allergic reactions, skin hives, red eyes, and eye redness. Lethargy, heart problems, and lung hemorrhaging are quite rare conditions in people infected by black mold, but you should be aware of them.
Black mold can affect the brain and lead to dizziness, lack of energy and concentration, and memory problems. They can cause swelling of the lymph nodes, muscle and joint problems, nose bleeding, loss of hair and even poor appetite.
Pregnant women should not be exposed to black mold, because it can cause many health problems, for both the expecting mom and the unborn baby. Toxic black mold can lead to miscarriage, anaphylactic reaction, choking, night sweating, cold, and even early menopause and MS (multiple sclerosis).















Your thoughts on this
Loading...