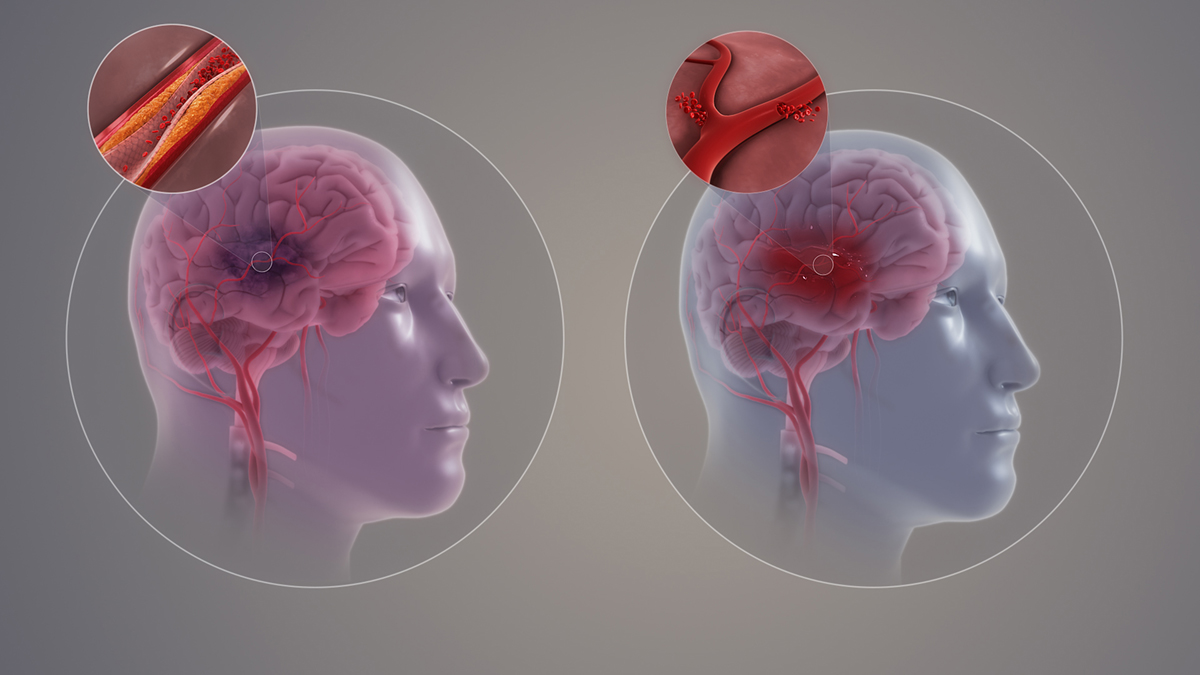
Brain hemorrhage is rather severe and life-threatening condition. Bleeding inside the brain and endocranium may be induced by numerous diseases. Head trauma often leads to the intracranial bleeding. In case of head trauma a subdural hematoma may be formed. This collection of blood shows symptoms similar to those present in brain hemorrhage. Basically the blood originates from the blood vessels of the brain. Only in cases of brain tumors the blood originates from blood vessels of the tumor. The damage to the brain is either reversible or irreversible depending on the spot of the hemorrhage and the quantity of the shed blood.
If the blood is present inside the brain tissue the hemorrhage is referred to as intracerebral and if there is bleeding between the brain membranes the bleeding is referred to as subarachnoidal.
The symptoms of brain hemorrhage are various. What is common for all of them is that they develop suddenly. The headache is regularly present. This happens because the skull is like a ball which cannot expand and additional blood in the skull leads to increase of intracranial pressure. This results in headaches. The increased pressure also leads to vomiting. The characteristic of this vomiting is that it occurs without accompanying nausea. Patients are weak, may have difficulties while walking. If the bleeding occurs in the area of the brain which is in charge with the speech patient will present slurring speech and might even not be capable to speak. Similarly if the optic area of the brain is affected the patient will present the problems with vision. In case of large amounts of blood present the paralysis occurs. The paralysis affects one side of the body partially or completely. Seizures are equally present. They tend to appear in people who have never experienced seizures before. Additionally problems with swallowing, tremor and abnormal sense of taste may occur. In most severe cases the patient loses consciousness, a coma develops and the lethal outcome is inevitable.
The diagnosis has to be set immediately. This is done by physical examination, CT scan of the head and sometimes by MRI.
The treatment depends on the spot of the bleeding and the amount of blood. Patients are always hospitalized. Certain medications are administered intravenously as most of the patients are comatose and cannot swallow. Majority of the patients are treated surgically. All those who survive this horrible condition have to go through long-term physical therapy in attempt to restore the damaged functions.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...