Introduction
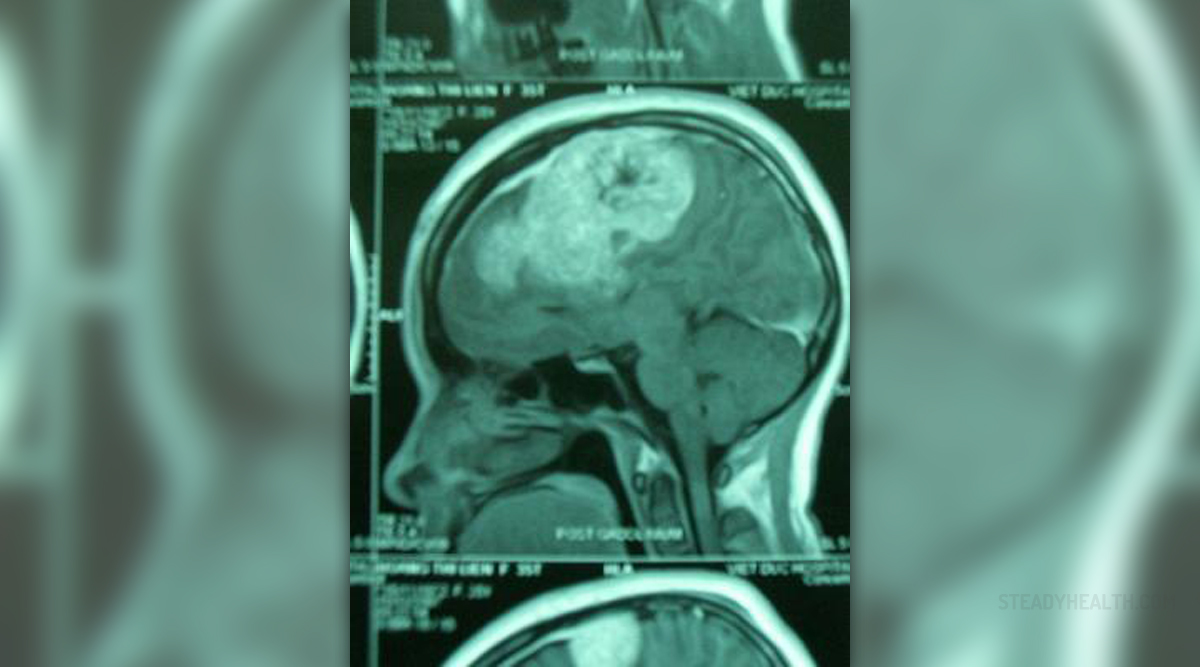
Meningioma is a brain tumor that originates from meninges. Meninges are the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. The truth is that meningioma is actually benign tumor. Still it can grow to the certain extent and cause severe complications. Therefore it acts as malignant tumor in certain number of patients. The size and the very location of meningioma is what determines the symptoms and signs of the disease. In some cases there can be more than one meningioma present.
The treatment of this tumor includes surgery and radiotherapy which is conducted after the surgical removal of the tumor. In patients who have small meningiomas and do not have any symptoms at all the surgical procedure is not performed unless the tumor starts growing or induce specific symptoms and signs.
Symptoms
Meningioma may not have to produce any symptoms at all. In other patients seizures, problems with eye sighs or hearing can occur. The weakness of ipsilateral extremities in elderly people can be mistaken for the stroke. Seizures can be in a form of Grand mal or Jacsonian seizures. Visual changes occur if the tumor is near the optic nerve or chiasma. Double vision and blurred vision are most commonly present. In certain cases if acoustic nerve is affected by the tumor the hearing problems may occur. In large tumors there is an obvious change in person's personality. Memory loss and impaired thinking are only some of the possible changes. In case that meningioma leads to increased intracranial pressure the patient will vomit and have severe headaches.
Surgical Treatment
As it has already been mentioned the surgical removal is performed in patients with large tumors, those with evident and intensive symptoms and those whose tumors are rapidly growing. The surgical removal tends to eliminate the whole of the tumor if possible. In some cases because meningioma is way to close to certain structures the tumor is only partially removed.
In some cases the tumor may form again. In case that parts of tumor remained in the skull postoperative radiation therapy is conducted. This reduces the risk of recidives.
There are several possible complications of the surgical procedure. The brain tissue around the tumor may be damaged. Hemorrhage and infections are additional complications that can occur.
Swelling of the brain is common after the surgery and is dealt with certain medications.
In certain number of patients seizures may occur after the surgery. If seizures were not present prior the surgery they can be considered as a complication.
And finally, there are even more severe complications such as problems with speech and coordination.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...