Gout
Gout is a medical condition in which uric acid accumulates in the joints. The leading symptom is inflammation of the affected joint. People who are suffering from gout experience recurrent attacks of the disease with occasional remission.
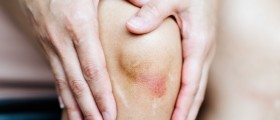
The symptoms and signs of the disease develop suddenly. Many patients have reported the onset of the disease during the night. The most prominent symptom of gout is excruciating pain in the affected joint. The inflammation most commonly affects ankles, hands and wrists, knees or feet. In podagra, which is a special form of gout, the big toe is affected by the process of inflammation. The skin above the joint may be swollen and it is red and warm. After the attack the skin above the affected joint may become itchy. In some patients increase body temperature has been reported. And finally, the diseases may be accompanied by development of specific nodules called tophi which usually affect elbows, hands and/or ears. The symptoms of the attack may withdraw spontaneously if a patient is not treated with certain medications.
Causes of Gout
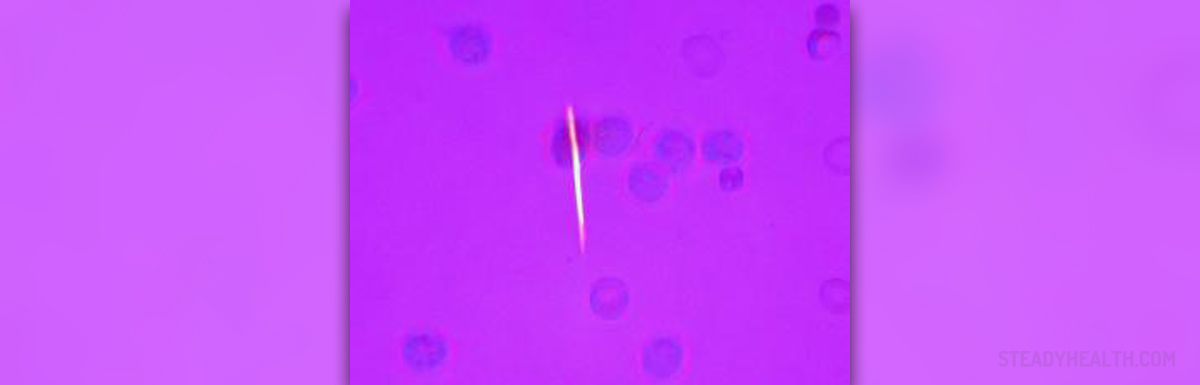
The actual cause of gout is connected to uric acid. This acid is normally excreted in urine. Still, in some people this acid may accumulate in the body. If it accumulates in joints it can cause gout. Hyperuricemia features with increased level of uric acid which consequently results in its accumulation. Uric acid is responsible for inflammation of the affected joints and the resulting pain.
Uric acid originates from chemicals called purines. They are found in human body and can be also taken with some food. Foods that are rich in purines include organ meats, anchovies, mushrooms, asparagus and many more.
Apart from hyperuricemia there are additional factors which may contribute to the onset of the disease. They include obesity, chronic alcoholism, enormously low calorie diets and regular intake of Aspirin, niacin or diuretics. Even certain medications which are used in patients who have undergone organ transplantation may induce gout. Gout may accompany some other medical conditions such as hypertension, chronic renal disease, hemolytic anemia, psoriasis, cancers and myeloma, hypothyroidism, and so on.
Prognosis of the Disease
Gout most commonly does not cause any serious problems apart from pain in joints. Still in some people this condition may become recurrent. Luckily, there are certain medications which can help in reduction of the attacks. These drugs may even completely eliminate the gout attacks.
If gout is left untreated the patient may end up with specific nodules under the skin. They represent accumulated urate crystals and are called tophi. These nodules become edematous and painful during every attack of the disease.
Hyperuricemia can additionally cause formation of kidney stones.
In some patients the affected joints are significantly damaged which reflect on their function. And finally, the disease may spread and affect other joints.



-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...