Gout is condition that causes inflammation of the joints, which become swelled and painful. Any joint can be affected - heel, instep, ankle, knee, finger, wrist or elbow, but most common place of gout attack is in the big toe. About one percent of population suffers from gout.
Symptoms of Gout
Typical symptoms of gout include severe joint pain, swelling of the joint and feeling of warmth in the area of affected joint, mild fever, presence of firm white lumps under skin (uric acid crystals, or tophi) and red, shiny skin in the affected joint area. Consult a specialist if you have these symptoms.
Gout attack is referred to as manifestation of gout symptoms. Gout attack usually lasts for up to two weeks and than recedes, even without treatment. It can recede within a week if treated. Gout attack may come only once in a lifetime, but it usually returns.
Complications of Gout
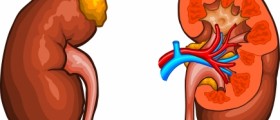
In very rare cases, gout can affect several joints (polyarticular gout), cause kidney stones (if urate crystals collect in the urinary tract) or kidney damage (if urate crystals collect in kidney tissue). Tophi can also cause inflammation and discomfort.
Causes of Gout
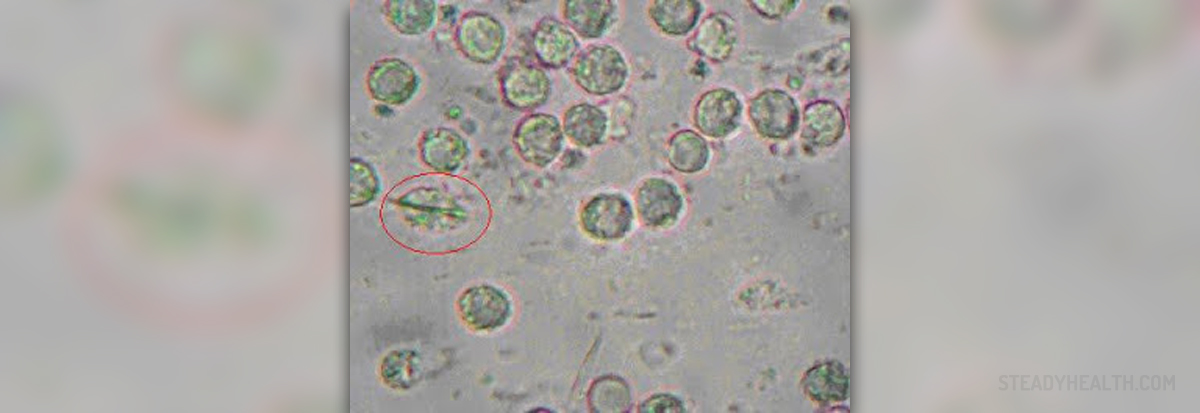
Gout is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the organism. Uric acid, or urate, is a waste product from metabolizing purines (organic compounds present in DNA of all cells and abundant in some foods, which is unrelated to DNA). Excess uric acid is normally filtered through kidneys and ends up in urine and gets expelled by urination. However, if for some reason there is too much production of urate or if kidneys don't filter out urate with sufficient speed, urate crystals can be formed and deposed in tissues, especially in or around joints.
Urates need lower temperature to crystallize and therefore form in cooler body regions such as fingers and joints. There are people who have increased uric acid level but never experience gout. Why gout occurs is still unknown. However, it is known that certain factors that increase risk of gout, such as sex and age (i.e. men are more likely to suffer from gout, typically between ages of 30 to 60), hormonal status (post-menopausal women), heredity, alcohol abuse, improper diet (too much red meat and seafood, being overweight), use of certain medicaments, or condition such as kidney disease, psoriasis, high blood pressure or injured joint. It is even possible to have a gout attack for no apparent reason.



-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...