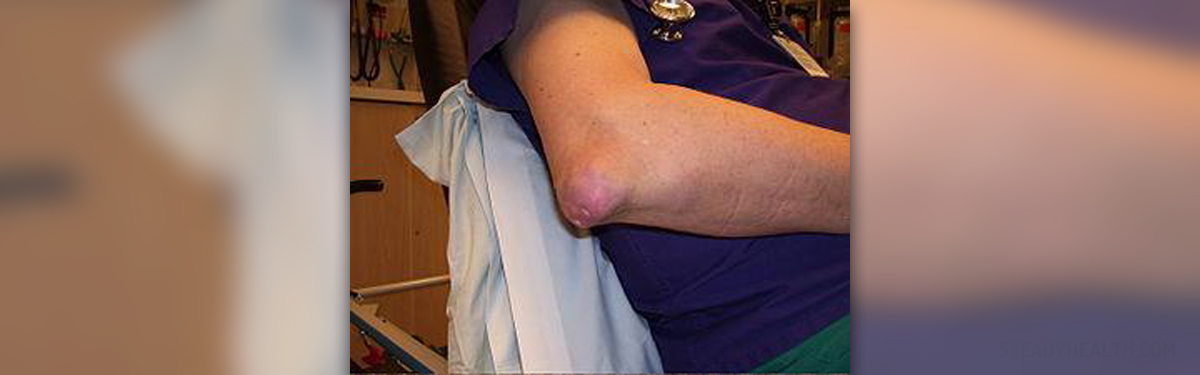
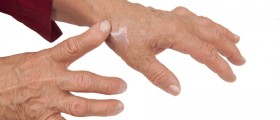
About gout
Gout is a disease that results from too much uric acid in the body or hyperuricemia. When there is too much uric acid, it starts to crystallize in the body, in tissues and especially in the joints. Accumulated crystals in joints cause recurring bouts of joint inflammation or arthritis.
Gout is a chronic and progressive disease, leading to more and more joint damage, but also to formation of kidney stones and to kidney damage.
Causes of gout
Gout, which is one of the most reported medical conditions throughout the history, is often associated with the body’s inherited inability to normally process the uric acid. Uric acid is actually the product of the breakdown of purins, which are found in many foods. When the body is unable to deal with uric acid, tiny crystals of urate form clumps that deposit in the joints.
However, hyperuricemia may also be diagnosed through blood tests, without any other problems, such as arthritis or kidney problems. This basically means that elevated levels of uric acid may be asymptomatic, but if the levels are not regulated and brought back to normal, they may eventually lead to gout.
Gout is characterized by recurring bouts of arthritis, with very painful and swollen joints and their limited mobility.
Treatment for chronic gout
Two key concepts in treatment of chronic gout involve impeding and reducing the joint inflammation that leads to gout attacks and applying a long-term strategy for management of gout in order to prevent recurring attacks. Both concepts are equally important in dealing with chronic gout.
Gout attacks are usually treated with anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce the inflammation and relieve the pain, restoring at the same time the mobility of the affected joint. Prevention of future attacks is mainly achieved by drinking plenty of fluids, maintaining a healthy body weight, eating healthy and balanced meals and avoiding alcohol consumption. It is very important to always stay hydrated because dehydration is one of the major contributors to gout attacks.
Dietary changes also play an important role. The best diet for gout should be based on foods that are low in purines, since uric acid is the product of purine breakdown. Foods to avoid include shellfish and organ meats like liver, kidneys and brains. Other protein sources are not considered to increase the chance of gout attacks. Fructose, found in corn syrup and soft drinks such as soda pops, should also be avoided.


-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...