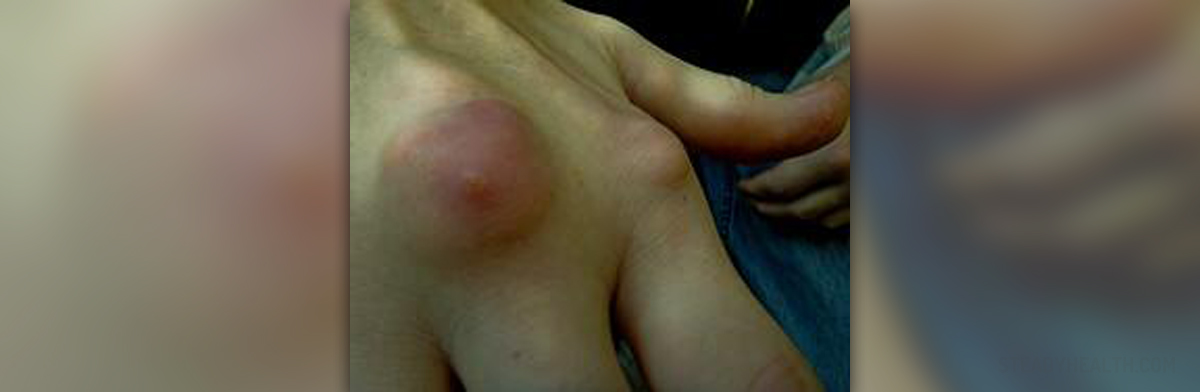
Gout is a peculiar medical condition responsible for sudden and severe attacks of inflammation of certain joints. This inflammation is accompanied by redness of the inflamed area, pain and reduced mobility. In majority of cases there is only one joint affected (the joint at the base of the big foot).
The attack typically occurs in the middle of the night. The pain in the affected joint wakes people up. It is generally described as severe burning sensation. One may notice that the joint is hot and it is also quite tender to touch.
Even though gout affects both genders, men are clearly more susceptible to the disease. The risk also increases in postmenopausal women.
The good thing is that people who have had a gout attack do not have to suffer from recurrent disease. There are highly efficient preventive measures that can successfully ward off repeated gout attacks.Gout Treatment
Treatment for acute gout attack usually requires medicamentous treatment. While some drugs deal with symptoms and signs of acute attack, others are rather efficient when it comes to prevention of disease recurrence.
The very attack is easily brought under control with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Initially one receives high doses of NSAIDs which are then gradually reduced.
Another drug frequently used during acute gout attacks is colchicine. The drug is most efficient when administered soon after the attack begins.
Finally, patients may receive corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are taken orally or can be injected directly into the affected joint. They are administered only if NSAIDs or colchicine fail to provide with desirable results.
Some patients need to take drugs that prevent complications associated with the disease like xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
Gout - Prevention
Prevention of future gout attack may be medicamentous or in a form of dietary changes. Even the combination of the two is possible.
Medications that prevent recurrent attacks are prescribed only in patients who have to deal with several gout attacks each year and those with less frequent but very painful attacks. These drugs are also necessary for prevention of potential complications of the disease in high-risk group of patients.Such individuals are prescribed low-dose NSAIDs or low-dose colchicine. They may be also prescribed allopurinol or febuxostat or even probenecid.
Dietary changes are of major importance for people suffering from gout. Namely, they reduce intake of foods rich in certain substances responsible for the onset of joint inflammation.
First of all, a person is due to drink plenty of water, at least 8-16 cups per day. Furthermore, intake of alcohol should be either restricted, if not completely eliminated. The foods one consumes should include fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low-fat (preferably fat-free) milk products. Meat, fish and poultry can be consumed, but moderately.
Finally, one will manage to control the disease if he/she maintains healthy weight. Loss of weigh can be an excellent way to reduce acid levels. Still, it must be gradual, never rapid. Rapid weight loss as well as fasting may be triggers for the increase in uric acid levels and the onset of gout attack.



-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...