
Uric acid
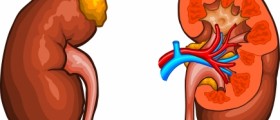
Uric acid is a waste productfrom metabolizing purines, molecules normally present in many foodsand in our organisms. In normal circumstances, there is a balancebetween production of uric acid and its removal by filtration in thekidneys. In some pathological states, for example, in some hereditarydiseases, too much uric acid is generated and the kidneys cannotremove it fast enough. Or, filtration ability of the kidneys might beimpaired, also as a result of some disease or condition, andotherwise normal amount of uric acid cannot be purged from the bloodat sufficient rate. As a result, excess uric acid is present in theblood. In such cases, uric acid can crystallize, forming tiny, needle-like crystals which accumulate in some tissues and in certainjoints. This condition is known as gout, and it is a form ofinflammatory arthritis.
Gout symptoms
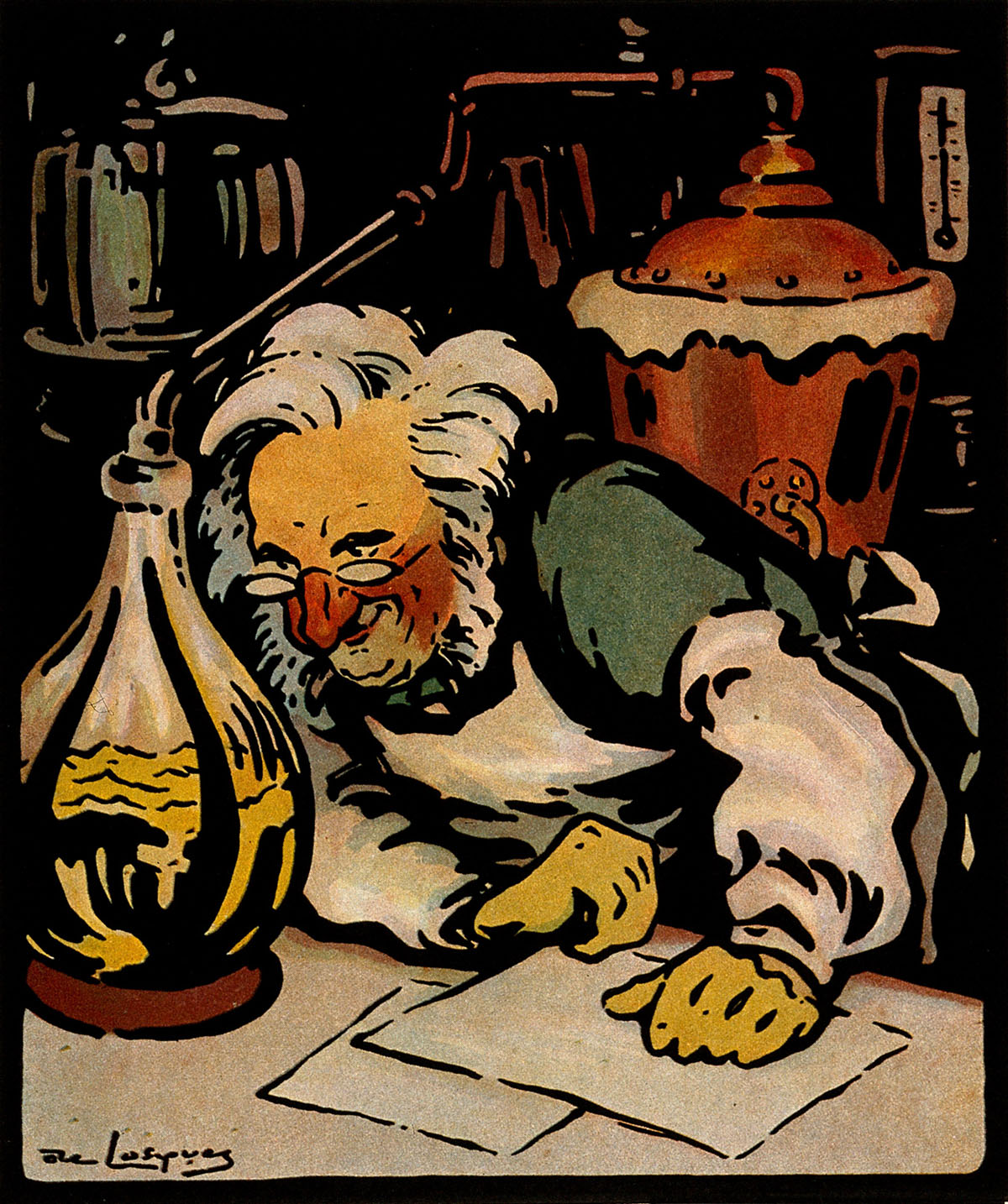
Deposition of uric acid isparticularly common in joints such as elbows, finger joints, ankle,knee or big toe joint. Affected joint (or joints) swell, becoming redand tender. Movement of those joints causes great pain. Crystals ofuric acid can also clog the filtering tubules in the kidneys, causingdisturbance in their function.
Causes of gout
There are various diseasesor conditions that can cause gout. Most common ones are lifestyle anddiet, meaning that people who consume food rich in purines (highprotein foods) or consume excess amounts of alcohol and caffeine areat higher risk. Medical conditions such as hypertension (high bloodpressure), diabetes and insulin resistance, arteriosclerosis andincreased levels of fats in blood also increase the risk ofdeveloping gout. some medications, such as, diuretics, can also causegout if used over a long period of time. Age and sex are also riskfactors, as it is known that men are more likely to develop gout,particularly those between 40 and 50 years of age. Women are mostlyaffected by gout after menopause.
Treatment
Once gout has beendiagnosed, it can be treated with various medications such asnonsteroidal anti - inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and others,depending on the recommendation of the doctor. Another very importantfactor in fighting gout is introduction to lifestyle changes. Youshould avoid purine - rich foods and increase amount of water thatyou drink. Also, avoid excess alcohol and caffeine. It is best toseek advice from a medical expert to see what prevention method suits you best.




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...