Gout is a painful form of arthritis featured by the intense attack of pain. Gout affects joints, mainly in the foot and it is most commonly the joint at the base of the big toe. During a gout attack, a person experiences sudden, sharp and burning pain, swelling and stiffness in a joint. Duration of the attack is between couple of hours to several days. Fortunately, gout can be treated and recurring attacks can be prevented.
Causes of GoutGout develops due to overload of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, substances naturally found in the body tissues and certain foods. High levels of uric acid in the blood can lead to formation of urate crystals that build up in a joint and surrounding tissue. Left untreated, crystals of uric acid can develop into nodules known as “tophi” that can be felt under the skin or in the joints. Gout can be caused by kidney stones, chronic kidney disease, heavy alcohol drinking, obesity and use of certain medications.
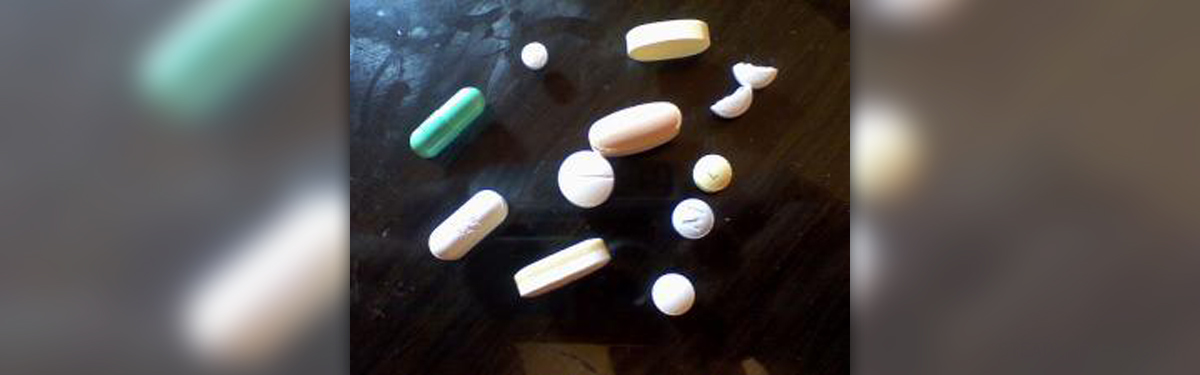
Gout Medications
To reduce the uric acid level in the blood a doctor will prescribe Zyloprim, gout medication that acts by limiting the amount of uric acid that is produced by the body. Corticosteroid medications such as Prednisone, prednisole and triamcinolone are given to reduce the pain and inflammation. Uric acid removal can be encouraged with probalan that stimulates the kidneys to eliminate uric acid from the body via urine. Medications given to control inflammation and pain in patients with gout are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Indomethacin, sulfinpyrazone, colchicines, corticosteroids, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), allopurinol and probenecid. All of the medications mentioned above are given to end gout attack, relieve the symptoms, prevent future attack and reduce the risk of gout complications such as tophi, kidney stones and deformation of a joint.
Side Effects of Gout MedicationsAllpurinol, one of the NSAIDs, entails adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion, dizziness, hair loss and headache. More severe side effects of this drug include fever, chills, blood in the urine and stool, fatigue, muscle pain, mouth ulcers, jaundice, wheezing, and seizures. Allpurinol may also cause an allergic reaction that will cause hives, difficulty breathing, itching, skin rash, swelling of face, tongue and lips. Use of colchicine can cause diarrhea, appetite loss, pain in the abdomen, nausea and vomiting. Colchicine toxicity can lead to kidney failure, muscle weakness, respiratory failure and hypovolemic shock. Prolonged use of this drug can cause number of serious medical conditions such as pancytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia, bone marrow damage, renal failure and glomerulonephritis. Corticosteroids can cause weakening of cartilage and deterioration of the joints.



-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...