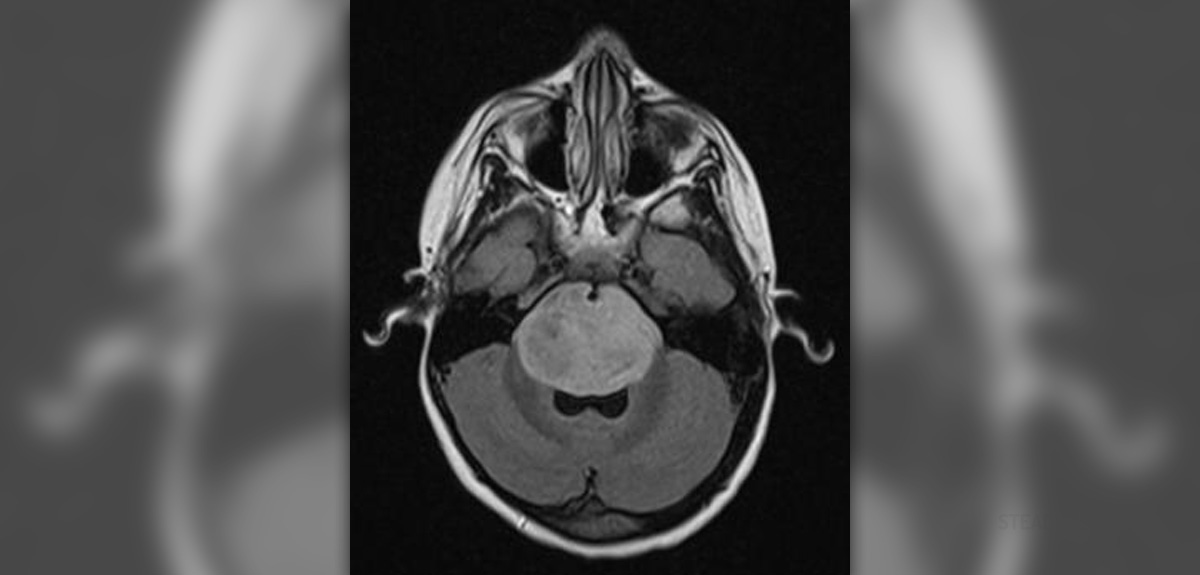
Benign tumor in the brain is a growth made up of cells with abnormal growth pattern and abnormal cell division but it is not cancerous. This means that the growth does not spread to and destroy nearby tissues and distant organs in the body. Benign tumors typically grow slowly. Benign tumors in brain are usually detected during CT or MRI brain scans as they often have visible borders of edges.
In general, benign tumor in brain is not a serious condition because it rarely develops into malignant tumor. In most cases, benign brain tumors can be surgically removed.
What exactly causes benign brain tumors is still unexplained but researchers believe that exposure to radiation or chemicals as well as family history increase the risk of their development.
Symptoms of Benign Brain Tumor
Most symptoms of a benign brain tumor arise from pressure that the growth puts on the brain tissue and other structures within the skull such as blood vessels, nerves and ventricles.
Benign brain tumor does not have specific symptoms as the symptoms often mimic those of other diseases. There are several symptoms produced by a benign brain tumor that may occur alone or combined. Headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and seizures commonly accompany benign brain tumor. Partial visual and hearing loss can be present as well. A person with benign brain tumor also often suffers from balance problems and numbness in extremities. Personality changes that manifest in abnormal behavior as well changes in mental ability such as speech problems, difficulty in concentrating and memory problems are common too.
Types of Benign Brain Tumor
The most common benign tumors in the brain are:
Meningioma - a type of brain tumor that grows on the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. About 20% of all brain tumor patients are diagnosed with meningioma. Schwannoma or acoustic neuroma – tumor that arises from the acoustic nerve, which regulates hearing and balance. This type of brain tumor accounts for around 9% of all brain tumors. Pituitary adenoma – it is a tumor that grows on the pituitary gland and accounts for around 8% of all brain tumors. Hemangioblastoma – it is a benign growth that develops on the brain blood vessels and accounts for about 2 % of all brain tumors. Craniopharyngoma – it is a cystic tumor that grows around the base of the brain and often affects children. Choroid plexus pailloma – a rare benign growth that arises from the choroid plexus and is usually diagnosed brain tumor in children.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...