Germ cells normally develop inside the fetus and once the baby is born they eventually mature and start producing sperm in men while in women such cells are necessary for production of eggs. Germ cells start their development along the 'midline' of the fetus and they eventually reach the location of reproductive organs. Abnormal grouping of these cells may eventually result in tumor formation. In majority of cases germ cell tumors occur in the testicles and ovaries (normal site of germ cells) although they may also form in other areas if these contain germ cells which have settled during fetal development.
Types of Germ Cell Tumors
All germ cell tumors are classified into benign and malignant.
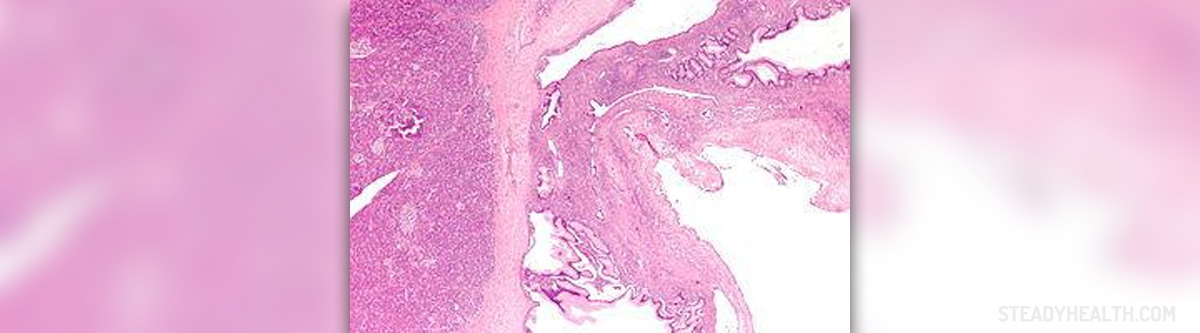
Teratomas are predominantly benign germ cell tumors. Still, they may also occur in a malignant form. In children, teratomas usually develop in the tailbone.
Germinomas are malignant germ cell tumors. Germinomas may affect both genders. Still, they are frequently found in the ovaries of girls in puberty.
Endodermal sinus tumors, also known as yolk sac tumors, can be both, malignant and benign. Malign endodermal sinus tumors are quite aggressive and hard to treat.
Embryonal carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating from germ cells and represents a mixture of different cell types.
And finally, choriocarcinoma is a strictly malignant tumor made of germ cells. It actually originates from the placenta and may soon spread to different organs (most commonly the lungs).
Causes of Germ Cell Tumors
Scientist have not managed to figure out why these tumors occur. Still, there are certain conditions which make children more susceptible to germ cell tumors. Some of them are birth defects of the central nervous system and other organs (genitals, urinary tract etc.). Children suffering from genetic disorders are also prone to germ cell tumors. And finally, undescended testicles represent a risk factor for this type of tumors.
Clinical Characteristics of Germ Cell Tumors
Symptoms and signs of germ cell tumors depend on several factors such as the location and size of the tumor, progression and growth of the tumor as well as its pathohistological type. Malignant forms grow rapidly and induce a variety of symptoms while benign tumors grow slowly and remain asymptomatic for a long period of time.Diagnosis and Treatment for Germ Cell Tumors
Diagnosis of germ cell tumors requires many diagnostic procedures. Doctors perform physical examination, imaging studies (X-ray, CT scan and MRI), blood tests and biopsy of the tumor. Biopsy is essential for final confirmation and it provides with full data regarding tumor's pathohistological type.
Treatment for germ cell tumor depends on several factors but it is definitely more aggressive in case of malignant form of the disease.
Benign tumors are treated surgically and removed in total. On the other hand, malignant germ tumors require more extensive surgery and additional treatment such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...