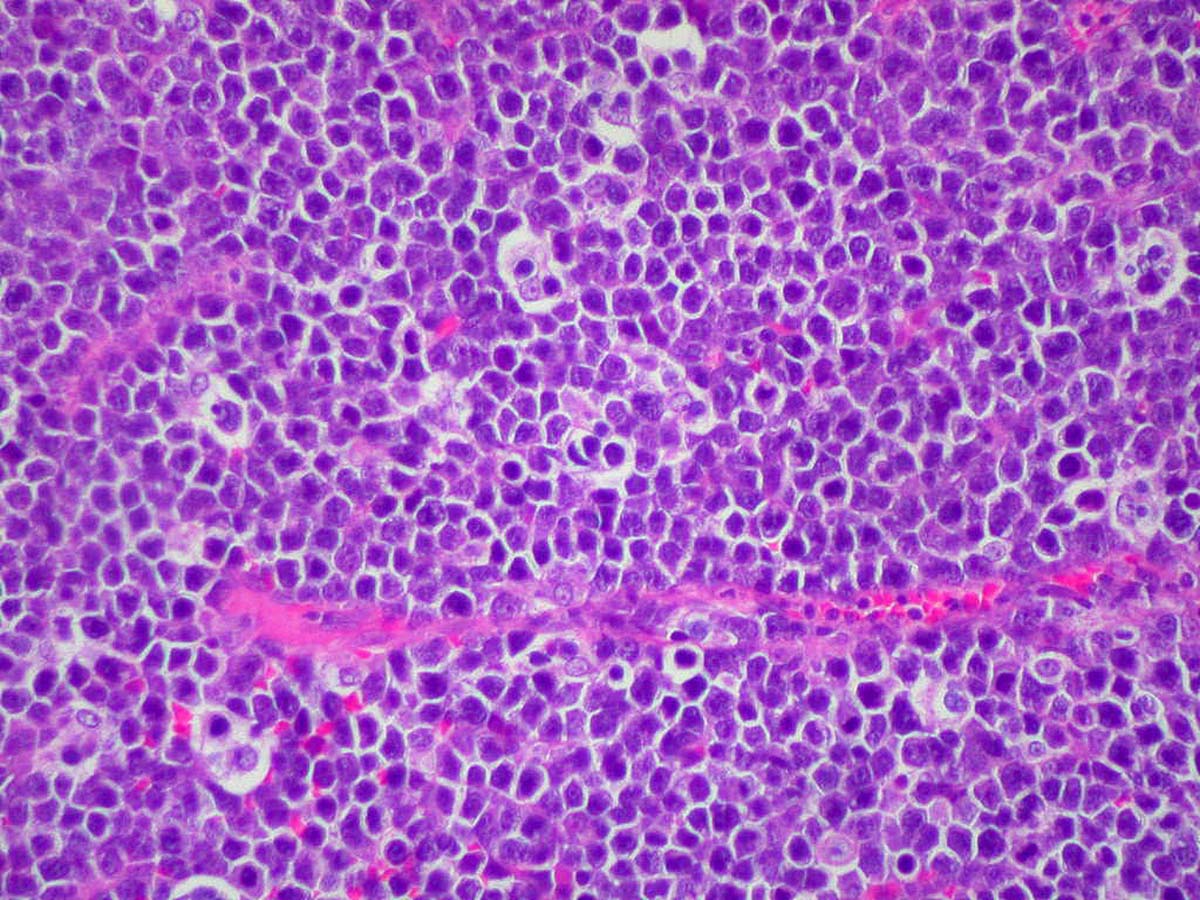
Burkitt lymphoma is a form of B-cell lymphoma. It was named after a British surgeon Dennis Burkitt, who first described the disease in 1956 during his work in Africa. Later a connection was found between previous infection caused by Epstein Barr virus and Burkitt lymphoma. Namely the children in Africa previously infected with the virus developed the lymphoma. What was evident is that many of the children had chronic malaria infections. This reduced the resistance to the virus, and sometimes the virus changed the infected B lymphocyte into cancer cell. This form of lymphoma is classified as African or endemic Burkitt lymphoma. One form of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is featured with the tumor cells which microscopically resemble those of classic African/ endemic Burkitt lymphoma. This form of lymphoma is classified as sporadic or non- African type of Burkitt lymphoma.
The disease most commonly starts in abdomen and is followed by abdominal swelling. It may also affect other organs like eyes, ovaries, kidneys, glandular tissue of the breast, thyroid gland or tonsil. The African/ endemic type starts growing in jawbone. From there it spreads towards nervous system causing neural symptoms.Beside evident or not obvious swelling the symptoms include night sweating, unexplained high temperatures and loss of weight.
The diagnosis is set after removal of the enlarged lymph node or a mass and its pathological examination. Sometimes only parts of enlarged lymph nodes are taken by biopsy. The patient has to undergo additional test such as complete blood count, chest X-ray and CT scan of the affected part of the body. Doctor conducts lumbar puncture and takes bone marrow samples. All of this is done to stage the disease since the treatment depends on the very stage.
Staging system used nowadays is \"St. Jude Modification of Ann Arbor\". There are 4 stages depending on how many groups of lymph nodes are involved, their location in the body and whether other organs like bone marrow or liver are affected. Today lymphomas are for practical purposes characterized as low-grade and high-grade. First ones are usually slow in growth. High grade lymphomas are more rapid in progress. Burkitt lymphoma classifies as high-grade lymphoma.
Treatment of Burkitt lymphoma includes chemotherapeutics. These cytotoxic medications are combined depending on the stage of the disease and possible additional conditions but there are fixed combination of these drugs called protocols that are in usage. They are administered intravenously during hospitalization. In case of spreading of the disease into the nervous system chemotherapeutics are administered intrathecally. Some of the chemotherapeutics include cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, methotrexate, cytarabine, ifosfamide and etoposide. Monoclonal antibodies are medications that recognize and cling to specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells. In that way the immune system is simulated to destroy the cancer cells. These drugs are given usually together with chemotherapeutics. Sometimes radiotherapy is conducted. The side effects of all the treatments are intensive and severe. Additionally to basic treatment supportive medications are included as well.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...