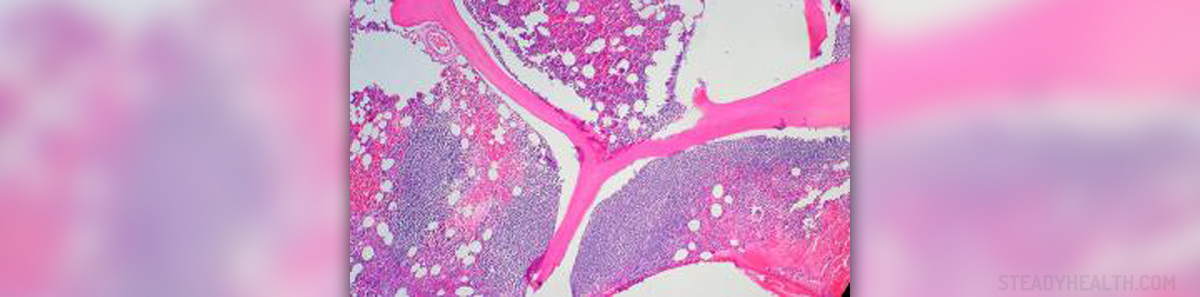
Follicular Lymphoma IntroductionA type of white blood cells known as lymphocytes an are important part of the body’s immune system. Lymphocytes are contained in lymph which circulates in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes and lymphatic organs such as the bone marrow, spleen and thymus.
Cancer of lymphocytes is called lymphoma. There are different types of lymphoma but two most common types are Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Follicular lymphoma is a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It is slow growing and usually does not have to be treated for many years.
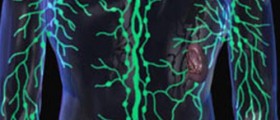
Symptoms of Follicular LymphomaFollicular lymphoma mainly affects lymph nodes. This type of lymphoma produces subtle symptoms thus may go undiagnosed until the cancer progresses. The most common symptom of follicular lymphoma are enlarged lymph nodes. This mainly occurs in the neck, armpits and groins. Enlarged lymph nodes are typically painless.
Other symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, high fever and night sweats. In advanced stages, follicular lymphoma spreads to organs such as bone marrow, liver, lungs or skin.
Treatment for Follicular LymphomaTreatment option for follicular lymphoma is determined by displayed symptoms, tumor grade, patient’s age and overall health. In most cases, the cancer is diagnosed when the disease is widespread. But, since follicular lymphoma grows slowly, it often does not require treatment in the initial stage. The treatment is generally not needed until the cancer starts producing symptoms. All in all, treatment approach in the initial stage involves only monitoring. Additionally, follicular lymphoma in early stage often does not respond to treatment unlike more aggressive types of cancer.
The treatment aims to relieve the symptoms. Treatment for follicular lymphoma is advised when there are progressively enlarging lymph nodes, fever, weight loss, sweating and low blood counts.
Follicular lymphoma is divided into four stages depending on the extent to which the cancer has spread. Cancer staging helps to determine the treatment option. Early stage follicular lymphoma (stage I or II) is often treated only with radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy involves the use of high energy rays to kill cancer cells. Involved field radiation is administered to the affected lymph nodes while extended-field radiation is administered to both the affected and surrounding lymph nodes.
Advanced stage follicular lymphoma (stage III or IV) can be treated with many treatment options. Treatment in advanced stage includes chemotherapy and monoclonal antibody therapy. Monoclonal antibodies are drugs that target and destroy cancer cells. A monoclonal antibody commonly used in treatment of follicular lymphoma is rituximab.
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells. This type of treatment is administered when the disease has spread to several lymph nodes and other organs. Follicular lymphoma often responds well to chemotherapy.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...