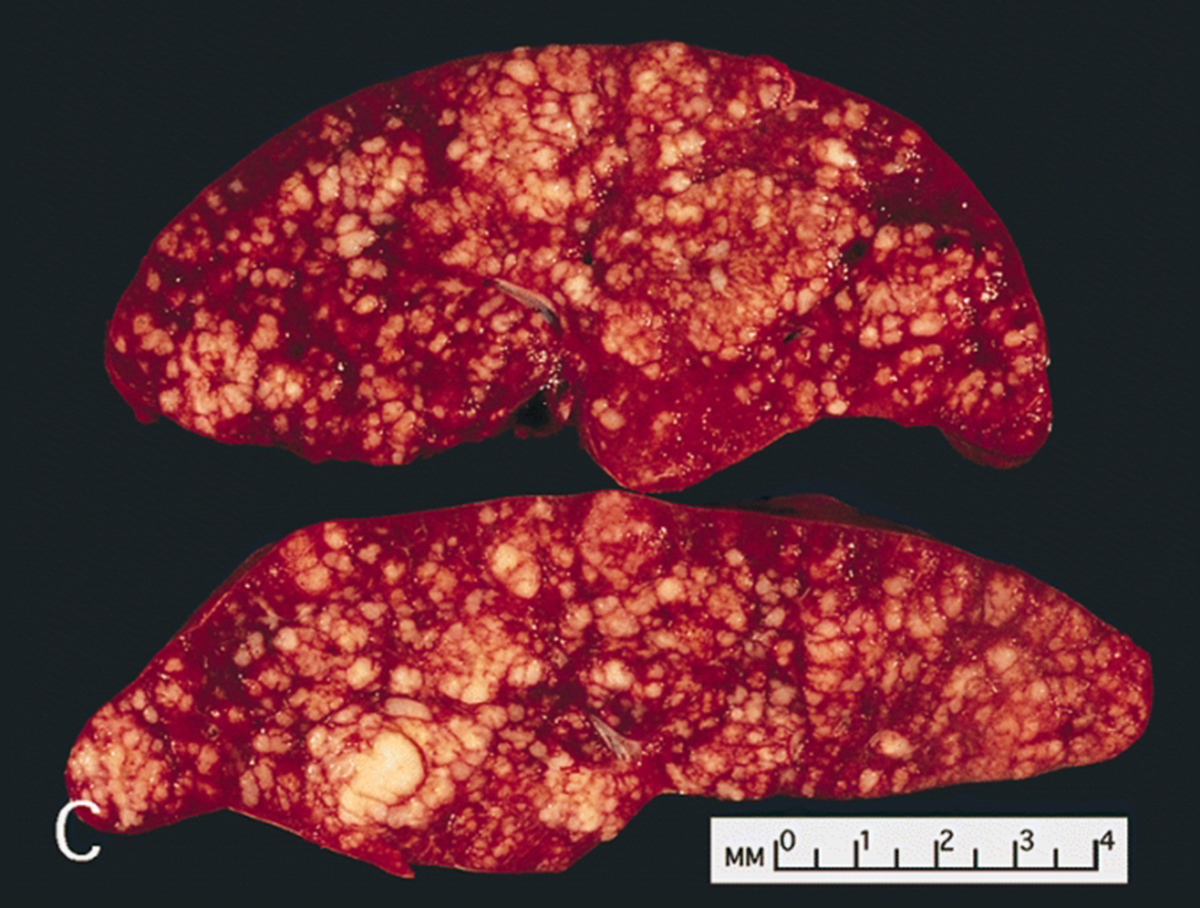
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a malignant disease of the lymphoid tissue and it basically affects the lymph nodes, spleen or other organs in the body. It includes any kind of lymphoma except Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Causes of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
In Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma the tumor cells originate from white blood cells that are normally found in lymphatic tissue. The majority of lymphomas originate from type B lymphocytes. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can be classified into 16 types. The tumor can be low, intermediate and high grade. Low grade Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is slow growing tumor and has much better prognosis comparing to high grade lymphoma where the tumor cells divide rapidly and the tumor grows quickly.
The actual cause of this malignant disease has not been identified yet. Still, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma usually affects people with weak immune system such as those suffering from HIV infection. It can also affect people who have undergone organ transplant surgery since they are on prolonged immunosuppressive treatment. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma usually occurs in adults and is slightly more common in men.
Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma features with a variety of symptoms. They basically depend on what area of the body is affected by the presence of the tumor. The symptoms also depend on the actual size of the tumor and the speed of its growth.
General symptoms of Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma include night sweats, occasional fever accompanied by chills, unintentional weight loss, loss of appetite and severe itchiness of the skin with no obvious skin changes. The tumor may affect any lymph node and lymphatic organ in the body and cause their enlargement and associated symptoms.
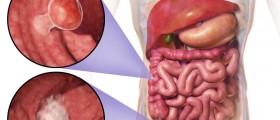
If the tumor has affected the thymus gland or mediastinal lymph nodes and has grown to significant size one may experience shortness of breath due to compression of the trachea. On the other hand, if the tumor is located in the abdomen patients may complain about abdominal swelling, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and constipation. The spread of the tumor onto the brain causes headaches, problems with concentration, personality changes and seizures.
Diagnosing Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
The doctor performs physical exam. This way he/ she may palpate superficial and enlarged lymph nodes. If internal lymph nodes have been affected this can be diagnosed with CT scan or MRI of different parts of the body. Blood tests are also performed and they are essential in measuring of certain protein levels and uric acid levels. One also undergoes liver and kidney function tests and bone marrow aspiration or biopsy. PET scan is highly effective in visualization of the tumor. The samples of the tumor taken during biopsy are pathohystologically examined.
Treatment for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
The treatment for Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma depends on the type of tumor, the stage of the disease and patient's general health.
The cornerstone of the therapy is chemotherapy. There is a variety of chemotherapeutics administered in patients suffering from Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Furthermore, radiation therapy is used to kill the tumor cells of a specific body area. And finally, some patients are treated with radioimmunotherapy. In radioimmunetherapy a radioactive substance is linked to an antibody that targets the tumor cells. This substance is then injected into the body.
Patients who do not respond to initial treatment are administered high-dose chemotherapy and subsequent bone marrow transplant with stem cells.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...