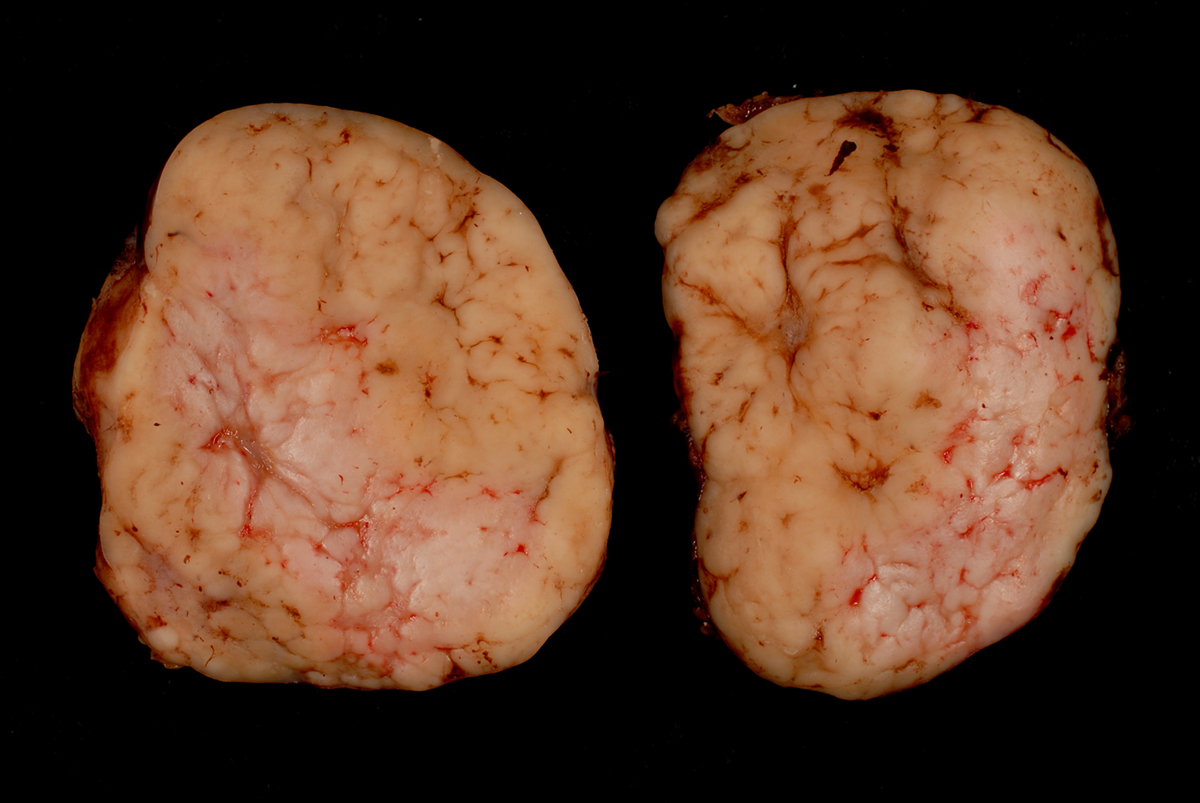
Hodgkin’s disease generally spreads downward from the initial state. It spreads from one lymph node to another but may also affect the bone marrow or the spleen. This disease is most common among people ages 15 and 35 years and people older than 55. Each year in the United States there are 7,500 new cases diagnosed. Hodgkin’s disease which accounts for less than 1% of all cancer cases in the US. The treatment for this cancer usually involves radiotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and bone marrow transplantation. However, the treatment depends on number and location of tumors, as well as the stage of the disease.
Causes and Risk Factors for Hodgkin’s disease
Exact cause of Hodgkin’s disease is unknown but there are some risk factors that increase the chance of developing this disease. The risk factors include age, family history, weak immune system and certain infections such as Epstein-Barr, Helicobacter pylori infection, human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV) and HIV virus.
Symptoms of Hodgkin’sdisease
The most common indicator of Hodgkin’s disease is painless swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, groin and armpits. A person affected by Hodgkin’s disease usually experiences fever and chills, persistent fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss. Weakness, coughing, trouble breathing, chest pain, itchy skin and soaking night sweats are also common in Hodgkin’s disease. Other symptoms include bone pain, enlarged spleen, red patches on the skin, sensitivity to effects of alcohol and pain in the lymph nodes after consumingalcohol.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Hodgkin’s disease can be made with the help of physical exam, where doctor check for enlarged lymph nodes and swollen spleen, and X-ray, CT scan and MRI scan to reveal location of tumor. Tissue sample (biopsy) of a swollen lymph node can provide definite diagnosis. The biopsy can also tell the grade of the cancer. Staging of Hodgkin’s disease depends on the location and number of the lymph nodes with Hodgkin’s disease cells and the presence of cancer cells in the bone marrow, spleen, liver or lung












Your thoughts on this
Loading...