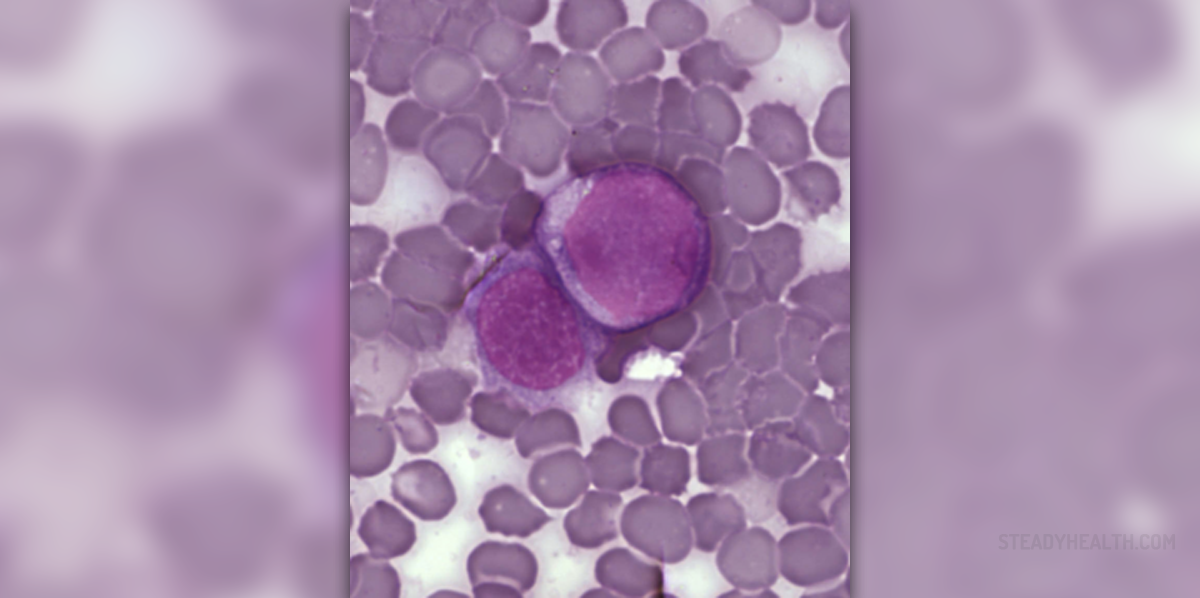
About Leukemia
Leukemia is a medical term that refers to a number of connected cancers that originate from blood forming cells of the bone marrow. It generally starts from white blood cells. There are several types of leukemia. All of them are initially classified into acute and chronic leukemia and further classification is based on the type of white blood cells that are affected. The second classification includes lymphocytic leukemia and myelogenus leukemia.
Scientists have not found the actual cause of leukemia yet, but they assume that the condition develops as a consequence of genetic and environmental factors. The cancer starts with an error, a mutation in the DNA of blood cells. These cells start to grow and divide uncontrollably and cause different symptoms and signs.
Symptoms of leukemia vary a lot depending particularly to the type of leukemia. However, many patients develop fever or chills, fatigue, weakness, suffer from frequent infections, lose weight etc. There may also be an enlargement of the spleen, lymph nodes and liver. Easy bleeding and bruising are two more characteristics of leukemia.
Therapy for Leukemia
Treatment for leukemia is not unique and generally depends on many factors. Patient's age, general health as well as the type of the leukemia and stage of the disease are major factors that determine the treatment. Chemotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for leukemia. There are several chemotherapeutics used in different types of leukemia and they can be combined. Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and preserve the healthy ones. However, they may also cause temporary damage to healthy cells which eventually recover. Chemotherapeutics are either administered intravenously or they are taken in pill form.
The goal of biological therapy for leukemia is to assist the body in recognizing leukemia cells and their destruction. Targeted therapy is a specially designed therapy. The drugs used in target therapy attack the specific vulnerable parts of the cancer cells not allowing them to multiply.
Radiation therapy is performed to treat tumor masses that did not respond to chemotherapy. Only the parts of the body infiltrated by the tumor are treated with radiation therapy. The doses are not high and cause no damage to the surrounding tissues. Radiation for leukemia may also be in a form of total body radiation, a procedure performed prior to the bone marrow transplant.
Some types of leukemia are treated with interferon. This is a class of proteins able to reduce leukemia cell proliferation and may also strengthen the body's immune response.
And finally, bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants are procedures in which the diseased bone marrow is replaced with a healthy one.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...