A non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a cancer affecting a crucial part of our immune system, the lymphatic system. This system spreads all around our body and, when one is suffering from a non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, the number of lymphatic cells rises uncontrollably or the cells themselves die slower than other cells in the body. There are many types of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas or NHLs.
Types of NHL
One common type of these lymphomas is referred to as aggressive. Also, it can be called high-grade lymphoma or intermediate-grade lymphoma. These are quite dangerous, spread rapidly and trigger numerous health issues.
Alternatively, slow-spreading, less dangerous type of lymphomas is called non-aggressive. Also, there is a difference between a non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and a Hodgkin's lymphoma. Basically, the NHL can appear at any possible location in the body, starting in a single lymph node or a group of these nodes. Furthermore, it may affect an internal organ and spread to other organs and parts of the body. This is why an early diagnosis of NHL is necessary for a successful treatment. Finally, NHL is not contagious and the causes of this cancer are still a mystery, even though many experts claim that it has something to do with infections in the body or exposure to environmental triggers.
Signs of NHL
Once a person is suffering from NHL, he/she has swollen lymph nodes in the neck, groin or armpit. Additionally, fever may affect this individual, without any other causes behind it. Furthermore, night sweats, tiredness, mysterious weight loss, itchiness of the skin and appearance of red rashes may signify NHL as well. Finally, shortness of breath, coughing or back and belly pain, all add on to the list of possible symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Biopsy is necessary for a proper diagnosis and the sample tissue is obtained from a lymph node in most cases. However, more tests may be necessary for definitive diagnosis.
Once NHL has been diagnosed, possible ways of treatment are observations, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibody therapy or stem cell transplant.
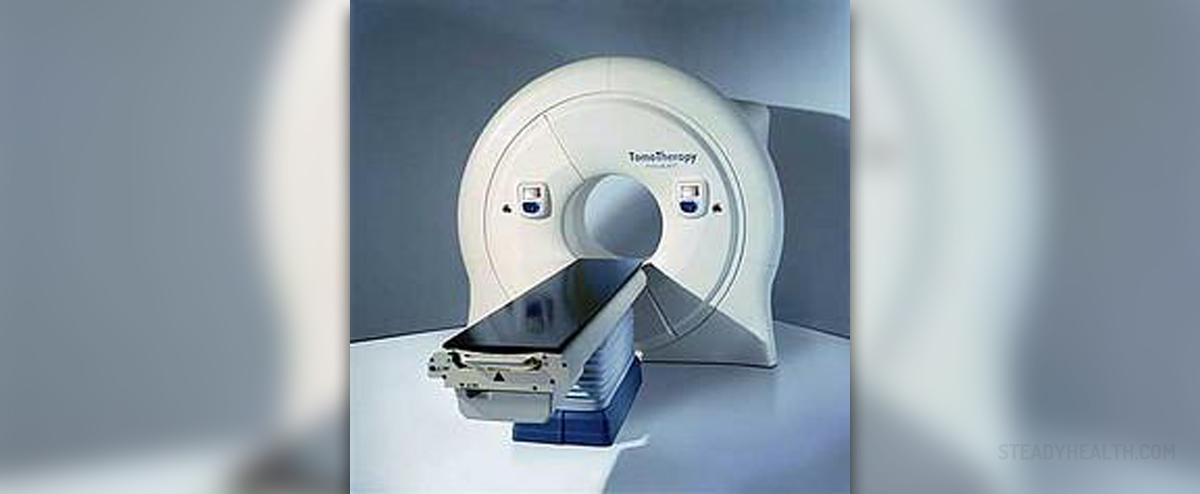
The radiation therapy is conducted by exposing the cancer cells to a high-intensity dose of X-rays. The radiation may be delivered from a machine located outside the patient's body, directed towards the affected spot, or it may be done from the inside with radiation coming from needles, wires and other such materials.
Since radiation is involved in this treatment, patients may experience certain side-effects once it is over. Low blood count, tiredness, redness of the exposed skin, hair loss, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, all may affect a person undergoing radiation NHL therapy.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...