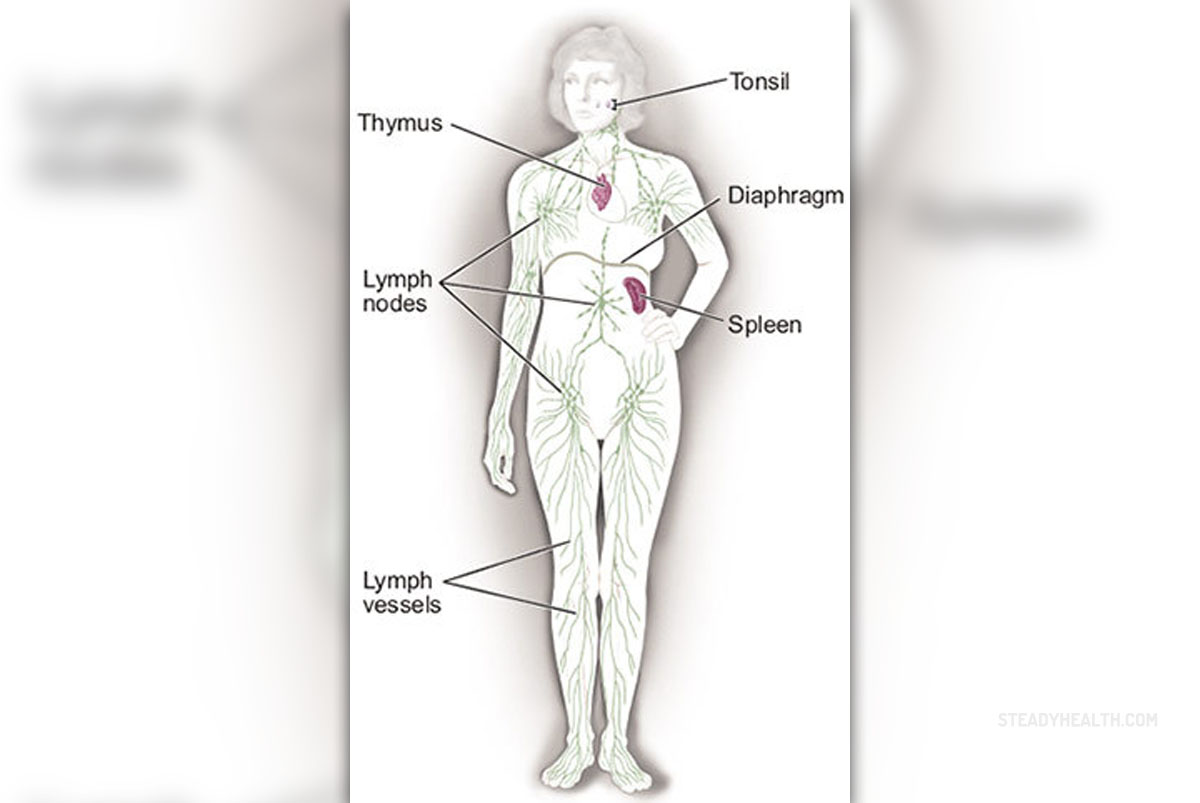
Lymphoma
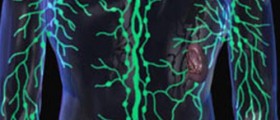
Lymphoma is a malignancy of lymphocytes (types of white blood cells), which usually begins in the lymph nodes or other lymphoid tissues. In addition to lymph nodes, which accumulate abnormal lymphocytes, the disease can be spread to the liver, the bone marrow, spleen and other organs.The disease can affect both children and adults. There are two main groups of lymphoma. Hodgkin's lymphoma (also called Hodgkin's disease) and Non Hodgkin's lymphoma. About 11% of patients suffer from Hodgkin's disease while the remaining number of patients suffer from Non Hodgkin's lymphoma. The number of patients with lymphoma is gradually but constantly growing.
Causes of Lymphoma
Although medicine has progressed a lot in terms of clarifying the causes of lymphoma, it is still difficult to prove a direct correlation with the appearance of lymphoma and some factors. Some viruses such as African Epstein Barr virus, HIV, viruses specific to Southeast Asia and Oceania such as HTLV type I are without doubt the best known culprits for the occurrence of lymphoma. But also, effects of radioactive radiation, organic solvents and other toxins as potential causes of lymphoma shouldn't be excluded. All these factors cause genetic damage to the cell converting it from a defensive cell in harmful, hostile and malignant lymph cell. It is possible that there are people who already have a genetic disorder, just waiting for the effect of radiation or other factors to increase the damage and complete all requirements for the transition to lymphoma.Symptoms and Signs of Lymphoma
The most typical sign of lymphoma is enlargement of lymph glands that are called lymphadenopathy. Enlarged lymph nodes in lymphoma are usually not painful, they are constantly growing and they are usually not reduced by routine therapy that is usually, prescribed by a general practitioner (antibiotics).You should bare in mind that not every lymphadenopathy leads to lymphoma. Lymph glands can be swollen as consequence of infection or any kind of inflammation. In these cases, the lymphadenopathy is the sign of accelerated production of lymphocyte immune cells.
But if lymphadenopathy cannot be explained by recent or still active virus, bacterial infection or nearby suppurative process, it should consider the presence of other symptoms such as: fatigue which is not caused by physical effort or psychological reasons increase in body temperature night sweating skin itching loss of appetite weight loss which cannot be explained by diet or increased physical activitybreath loss and persistent cough Diagnosis of lymphoma is based on biopsy, and treatment usually involves a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...