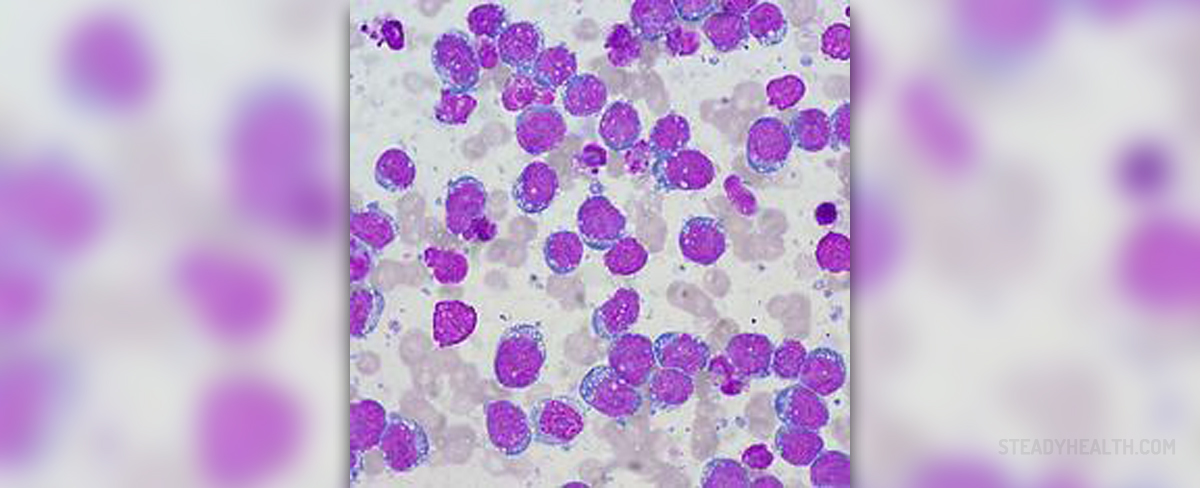
Cancers of the immune system are known as lymphomas and there are two distinctive lymphoma types, Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma causes abnormal growth of lymph nodes, affecting functioning of the lymphatic and immune system of the body. This lymphoma is also known to affect different organs of the immune system, causing additional health problems.
According to the type of white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes the lymphoma affects, there are B and T cells lymphomas. However, most of these lymphomas affect B lymphocytes. Another criterion for differentiation of lymphomas is the rate of growth and there are low-grade (indolent lymphomas that grow very slowly), high-grade (aggressive lymphomas) and also very high-grade (very aggressive lymphomas which grow extremely rapidly).
Symptoms and Treatment
Different people experience different symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. In most cases, patients notice swelling in the neck, under the arms or groins. There is no pain accompanying the swelling, but there are usually some enlarged lymph nodes in the affected area of the body. If lymphoma affects lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity, the patient might notice some increase in the belly region. Other symptoms that may indicate non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma include fever, night sweats, weight loss and fatigue. Patients who experience swelling of lymph nodes that does not respond to antibiotic treatment or which last for longer than 6 weeks may be suspected to have non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Treatment for this type of lymphoma depends on the aggressiveness of the tumor. Patients may be treated with chemotherapy or radiation if their non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is indolent. Both radiation and chemotherapy are usually used to resolve pain and fatigue more than to cure the disease. Aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma requires chemotherapy and cannot be cured. Indolent and aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas may also be treated with stem cell transplantation. Very aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma needs to be treated with urgent chemotherapy in order to prevent life-threatening consequences.
Causes and Possible Prevention
Although scientists and doctors cannot explain why, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is still on the rise in Northern America. So far, there are no identified reasons or factors for this type of lymphoma and no one can tell why this happens. The only thing doctors are able to say about this lymphoma is that it occurs more frequently in older patients.
Because of that, no one can tell what to do to prevent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The best course of action is to consult your doctor if you notice symptoms indicating non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and follow the treatment you get.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...