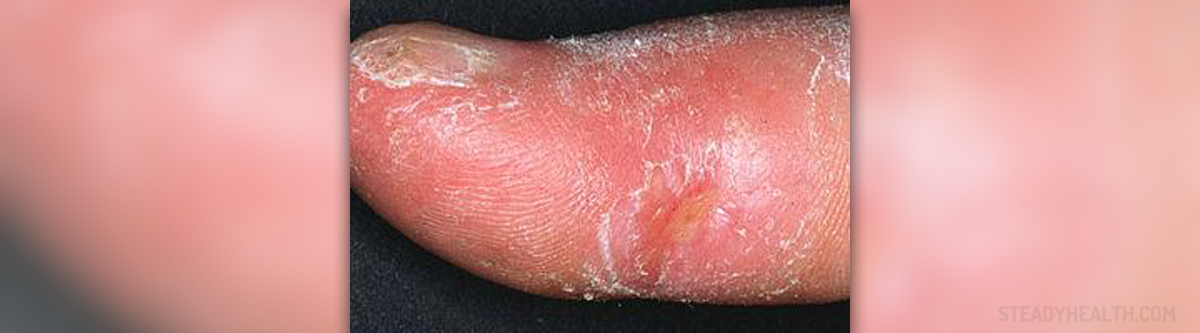
Systemic sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, is an autoimmune disease which affects many organs and organ systems such as the skin, blood vessels, muscles, lung, heart etc. This chronic illness features with diffuse fibrosis and accompanying degenerative changes. The condition predominantly affects women and usually starts in the 3rd to 5th decade of life.
Causes of Systemic Sclerosis
Systemic sclerosis is closely related to immunologic mechanisms and it is also considered a hereditary disease. The condition may develop as a consequence of exposure to vinyl chloride, bleomycin, pentazocine, epoxy and aromatic hydrocarbons.
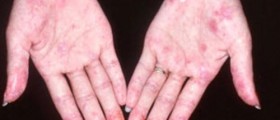
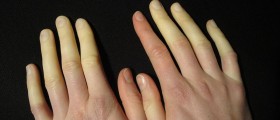
The main characteristics of the condition are connected with vascular damage and activation of fibroblasts. There is excessive production of collagen and extracellular proteins which eventually leads to symptoms and signs of the disease. The severity of the condition depends on the affected organ and the extent of damage caused by excessive production of collagen fibers.Clinical Characteristics of Systemic SclerosisPatients initially develop symptoms and signs of Raynaud's syndrome and serious swelling of the distal extremities. The skin of the fingers starts thickening. Swelling of the skin is symmetric. The affected skin eventually becomes taut and shiny and its color changes. Patients suffering from systemic sclerosis develop telangiectasias, subcutaneous calcifications and trophic ulcers. There is also pain located in many joints (polyarthralgia). Depending on the affected organ or organ system patients report different symptoms. Some of them complain about problems with the gastrointestinal tract while others have problems with the respiratory tract, joints, heart, kidneys etc.Therapy for Systemic Sclerosis
There are several treatments for systemic sclerosis. The doctor chooses the most convenient one according to complexity of symptoms and the affected organs.
Patients complaining about itchy skin can benefit from camphor and menthol, topical emollients, psoralen UV-A (PUVA) treatment or UVA-1 phototherapy. Patients suffering from calcifications are treated surgically( prolonged recovery time). In case of Raynaud's syndrome patients are initially suggested to avoid exposure to cold temperatures and are supposed to wear loose-fitting clothes and, if necessary, gloves and warm socks. Medicamentous treatment for Raynaud's syndrome include calcium channel blockers, vasodilating drugs, intravenous prostaglandins and prostacyclin analogs. Aspirin may be also prescribed.
In case the condition has caused damage to the kidneys the doctor may opt for ACE inhibitors while gastrointestinal symptoms and signs can be brought under control with proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers. Patients with respiratory symptoms and signs require calcium channel blockers, prostaglandins and cyclophosphamide. Myositis caused by systemic sclerosis is treated with corticosteroids.
Immunomodulatory agents commonly prescribed in severe forms of the disease include corticosteroids, methotrexate, chlorambucil, Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, thalidomide, low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide and statins. And finally, antifibrotic agents are currently evaluated as treatment option for systemic sclerosis. They include D-penicillinamine, interferon alfa and interferon gamma.
- www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/stem-cell-transplant-severe-scleroderma-improves-survival-quality-life
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/scleroderma/
- Photo courtesy of Frank Breuckmann, Thilo Gambichler, Peter Altmeyer and Alexander Kreuter by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Systemic_sclerosis_finger.jpg












Your thoughts on this
Loading...