
Lupus erythematosus may develop in several different forms and one of them is cutaneous lupus erythematosus. This is a nonscarring non-atrophy-producing photosensitive dermatosis. The condition may be the part of systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren syndrome or develop alone. Clinical Characteristics of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
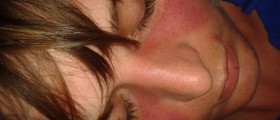
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is most commonly seen in patients suffering from systemic form of the disease. It typically leads to formation of a butterfly rash, rash that affects the face, to be more precise the one that is located on the nose and cheeks. It resembles a sunburn rash. Patients additionally develop generalized flat red patches on extremities and trunk. These lesions as well as the rest of the skin are highly sensitive to the sun. This is why skin changes predominantly affect sun-exposed parts of the body. Skin lesions of acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus do not cause scarring but may be responsible for changes of the color of the affected skin (hypopigmentation/hyperpigmentation). Apart from the previously mentioned, patients may also develop oral ulcers, hives and temporary hair loss. Since many of them also suffer from systemic disease, they suffer with different symptoms and signs of systemic lupus erythematosus.
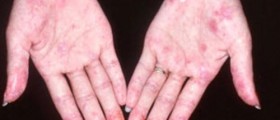
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus develops in a form of papulosquamous lesions and annular lesions. The first skin changes develop as red, scaly patches and may resemble psoriasis. Annular lesions are ring-shaped and may have scales on their edges. These non-itchy skin changes affect the chest and the upper back or neck. The face and the arms may be affected as well.
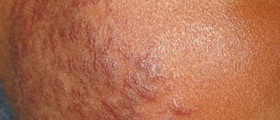
Many patients end up with chronic skin lesions. This skin condition develops in a coin-like shape rash. The skin lesions are thickened and in a form of red, scaly patches. They predominantly affect the cheeks, nose and ears. From these predilection sites, skin lesions may further spread to the neck, upper back and dorsum of hands. Skin lesions are neither itchy nor painful. Once the lesion completely heals, it leaves the affected skin with hyper or hypopigmenation. Atrophy of the affected skin is another characteristic of the disease. Cutaneous lupus of the scalp and other body parts may cause permanent destruction of hair follicles and hair loss. Patients also develop ulcers inside the oral cavity. They are dangerous because they may eventually transform into squamous cell carcinoma. Patients who develop skin lesions on the head and neck almost never end up with systemic disease. And finally, certain number of patients end up with lupus profundus (lupus panniculitis), a form of the disease in which the fat tissue below the skin gets affected by firm nodules. Resolution of these nodules is followed by indented scars called lipodystrophy.
Treatment
The goal of the treatment is to improve patient's appearance and prevent further skin lesions.
Treatment begins with sun protective measures which include constant use of sunscreens and protective clothing. In case there is vitamin D deficiency, the condition is brought under control with supplements.
The skin lesions are generally treated with topical or intralesional corticosteroids and antimalarial medications. Apart from that some patients may be prescribed auranofin, dapsone, thalidomide, retinoids, interferon and some immunosuppressive agents. Systemic corticosteroids are not the part of the treatment and they are only prescribed if an individual is also suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...