About Lupus
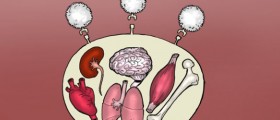
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory condition which results from abnormal response of the immune system. The body's immune system does not recognize its cells, attacks them and causes serious damage to a variety of organs and organ systems (kidneys, skin, joints, heart etc.). Therefore, lupus is classified as autoimmune disease.
There are several types of lupus - systemic lupus erythematosus, discoid lupus erythematosus, drug-induced lupus erythematosus and finally, neonatal lupus. The most serious type is definitely systemic lupus erythematosus. The condition predominantly affects women.
The actual cause of the condition has not been identified yet although many scientists agree that lupus develops as a consequence of a combination of genetic and some environmental factors. Predisposition to the disease may be inherited but whether the person will develop lupus or not generally depends on certain triggers.
We can say that lupus is unique since there are no two cases that are actually the same. Symptoms and signs usually develop suddenly but gradually. They vary in intensity and may be temporary or permanent. Lupus typically features with periods of flare and remission.
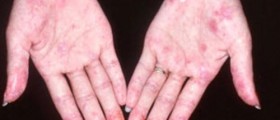
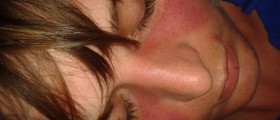
General symptoms of the disease include fatigue, fever, weigh changes, joint pain, stiffness and inflammation. Patients also develop a specific skin rash on the face called butterfly-shaped rash. Mouth sores, alopecia, circulatory problems, respiratory problems, mental changes (anxiety, depression, memory loss etc.) are several more characteristics of lupus.
Therapy for Lupus
Treatment of lupus depends on the severity of the illness and the intensity of symptoms and signs. The condition is generally brought under control with certain medications. The dose of these drugs is higher during flare-ups while in remission the dose is significantly reduced.
Mild to moderate forms of lupus are treated with three types of drugs. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the first group of drugs prescribed to patients suffering from certain types of lupus. Furthermore, antimalarial drugs are effective in case of discoid lupus erythematosus. And finally, in majority of patients the condition is treated with corticosteroids. Even though corticosteroids have serious long-term side effects they are highly effective against the disease. Doctors prescribe the lowest dose that can control the disease.
Some patients are prescribed with drugs for specific symptoms and signs of the disease such as joint inflammation, skin rashes etc. Aggressive form of lupus that leads to damage to vital organs such as kidneys, blood vessels, heart, lungs or the central nervous system requires more aggressive treatment. Such patients are treated with high-dose corticosteroids. And finally, in extremely severe cases doctors may opt for immunosuppressive drugs or try a combination of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...