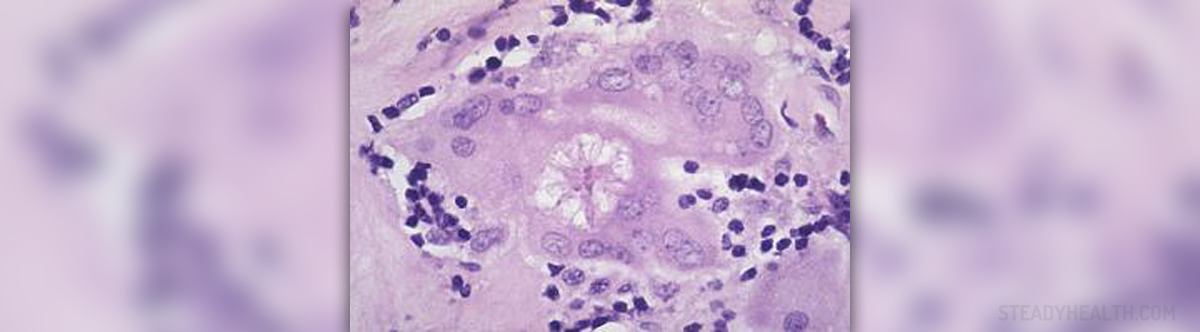
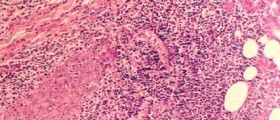
Sarcoidosis is a medical condition that features with collections of inflammatory cells in many organs in the body. These collections of inflammatory cells eventually form specific nodules called granulomas. The granulomas typically affect the lungs or lymph nodes. Still they may form inside other organs as well. Once the disease has occurred it develops gradually. It may improve and withdraw spontaneously. On the other hand, if the symptoms and signs of the disease persist and cause serious problems patients must be properly treated. Progression of the disease may eventually lead to lung scarring and infections and in extreme cases one may die due to respiratory failure. Sarcoidosis may be also fatal if the heart, nervous system, liver or kidneys are affected. The actual cause of sarcoidosis has not been identified yet.
Symptoms of Sarcoidosis
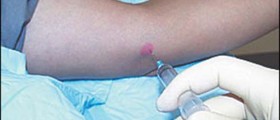
Initially the disease is asymptomatic and granulomas may be discovered accidentally during certain exams such as X-ray of the chest and similar. Definitive conformation of the disease is obtained after pathohistological examination of the granuloma which is surgically removed.
The symptoms and signs of sarcoidosis depend on the affected organ. General symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, fever and feeling of being ill.
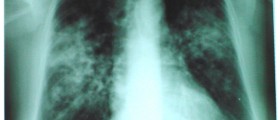
Shortness of breath and persistent cough are typical for sarcoidosis of the lungs. There may also be chest pain or feeling of tightness in the chest.However, if the disease affects the skin it may start with skin rashes. The skin lesions are usually in a form of small raised patches on the face. The patients may also develop erythema nodosum and it predominantly affects the skin of the face, arms or shins. If the disease affects the eyes there is evident inflammation of certain parts of the eyes. In sarcoidosis of the nervous system granulomas may be found in the brain, spinal cord, facial and optic nerve. In severe form of the disease sarcoidosis of the nervous system may cause serious neurological problems and facial paralysis is only one of them.
Treatment for Sarcoidosis
Certain number of patients actually does not require any treatment at all. Other patients are basically treated with corticosteroids. These medications have been prescribed for many years. It may happen that patients simple do not respond to corticosteroids. These patients are given steroid-sparing agents such as azathioprine and methotrexate. Cyclophosphamide is rarely prescribed. And finally, some studies suggested efficiency of immunosupressants, interleukin-2 inhibitors and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment in patients suffering from severe form of the disease.
All the patients suffering from sarcoidosis require specific follow-up. The disease may affect many organs and this is why doctors regularly control the function of many organs in patients suffering from sarcoidosis.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...